The Suppression of Knowledge
The basis for how we live our lives and understand the things around us, society, personal relationships, family values and the like, is rooted in what we are told by “the authorities”. Unfortunately, much of what you have been told is just not true. You have been lied to about science, astronomy, the environment, global warming, government, taxation, war, energy, inventions, education, terrorism, health, finance and the media, to name a few that spring to mind.
Science Astronomy The Environment Global Warming Government and Taxation War Energy
Home Inventions Education Terrorism Health Finance The Media Joseph H. Cater
has produced a book entitled
“Ultimate Reality” which is almost impossible to buy at any reasonable
price level. In it, he points out many things which he supports with
strong evidence. These things seem startling because, and only because,
the present educational system deliberately encourages us to believe
things which are clearly not true. Google books have a partial copy of
the “The Ultimate Reality” here
The things which Joseph Cater states are so unusual that it would be
easy to write him off as a crank. However, he backs up what he says,
with a considerable body of realistic evidence which makes it very
difficult to ignore what he says, in spite of the fact that most of his
findings flatly contradict what we have been taught from an early age,
and so accept as being reality. Whether or not you accept what he says
is entirely up to you, but it is difficult for an honest person to
reject his presentation out of hand.
He puts forward a strong case for there being a deliberate programme of
scientific misinformation and suppression aimed at keeping the general
public completely ignorant as to the actual physical realities of the
solar system and the universe in general, and as a result, reality is
very far from the popular conception. Mr Cater’s description of matter
provides reasoned explanations for a whole range of anomalies which
conventional science can’t adequately explain, and he quotes numerous
experiments which provide firm evidence that what he is saying has a
substantial basis in fact.
Here is a very brief summary of some of what he says in his book “The Ultimate Reality”:
The biggest single factor is in the erroneous theory of sub-atomic
particles. Mr Cater states that reality is actually much more simple
than conventional theory suggests. The universe is filled with a range
of energetic particles which he describes as “higher order ethers” and
“lower order ethers”. These ether particles are in continuous random
movement at different frequencies and they produce a number of different
kinds of composite particles including “Hard electrons” (with which we
are already familiar) and “Soft electrons” which have very different
properties. Soft electrons can draw hard electrons into themselves,
masking the properties of those hard electrons. Combinations of ether
particles form photons and all matter is composed of photons and these
ether particles.
The operational forces which govern all matter in the universe are only
electrostatic force and magnetic force, and the actions of both of these
are modified by many different combinations of the two types of
electron. As light is composed of photons and as they interact with the
two types of electrons, many observed scientific facts have led to
wholly incorrect deductions. Mr Cater indicates that the New World
Order “elite” carefully foster and support these false conclusions,
suppress information and physically alter observations before they reach
the public. Mr Cater points out a number of instances where the
alteration of data has not been sufficient to suppress the facts.
It is not possible to mention all of the points which Mr Cater makes, so
please understand that the following is only a minor selection from a
cohesive whole and much of the supporting evidence which he provides in
his book is omitted here.
Mr Cater says:
1. The current theory of gravity is completely wrong, and gravity
is caused by a component of the electromagnetic spectrum of about one
trillion cycles per second (0.3 to 4.3 mm wavelength; located above
radar and below the infra-red region). The theory of gravity put
forward by Sir Isaac Newton does not account for the amount of
deflection of a plumb bob near a mountain. An asteroid as small as 150
miles in diameter, can have a surface gravity about the same as Earth’s
and some asteroids have moons of their own orbiting around them. This
would be impossible if Newton was right.
As a result of the real cause of gravity, our Moon has a much higher
surface gravity than was expected, (and consequently, a serious
atmosphere). NASA had a major problem with the lunar landing of 1969
because if the real facts became known, then it would demonstrate that a
major section of physics, as it is currently presented, is incorrect
and they want to keep things exactly as they are at present. The Moon,
in common with most planets, is not solid. When part of the lunar
lander was dropped back on to the surface of the Moon, a seismic
detector left on the surface showed that the Moon vibrated like a bell
for about an hour afterwards. That would not have happened if the Moon
were solid.
There is very clear evidence that NASA has censored the Moon landing
very heavily, but their attempts at suppression have been flawed and
some obvious pointers exist. For example, NASA claimed that the space
suits of the astronauts weighed 185 lbs when on Earth. Photographs
exist, showing an astronaut leaning over backwards and then regaining
his balance. That would be a physical impossibility even under reduced
gravity, and this implies that the “life support” systems were actually
empty and not needed because there is an atmosphere. The high surface
gravity is also seen when the astronauts ran. Even the slowed-down
version released by NASA can’t conceal the length of the steps and the
height off the ground which are the same as they would be on Earth.
If the Moon had one sixth of the Earth’s gravity as is claimed by
conventional science, then the point at which the gravitational pull of
the Earth balances that of the Moon would be about 22,000 miles from the
Moon. The Encyclopaedia Britannica states this distance as being about
40,000 miles, which agrees with various other sources. That could only
be so if the Moon’s surface gravity were much higher than the supposed
one sixth of Earth’s gravity.
On more than one occasion, an Apollo astronaut tripped and fell on his
face. Under one sixth gravity, that just would not happen, especially
with a fit and active astronaut. Also, the rover vehicle used in later
landings was 10’ long, 7.5’ wide and 4’high with 32” diameter wheels.
The Earth weight was 460 pounds and under one sixth gravity, that would
only be 75 pounds, but the astronauts had great difficulty unloading it
from the lunar module. Engineers on Earth had already determined that
to operate under one sixth gravity, the rover would have to be 20’ long
and have a 20’ tread. With a loaded earth weight of 1,600 pounds, it
would need a turning radius of well over 80’ to avoid tipping over at 10
mph or more than 20’ at 5 mph and descending steep hills would not be
possible without major problems. But, the astronauts did descend steep
hills and they made very sharp turns at maximum speed.
One of the photographs brought back by the Apollo 12 trip, showed an
astronaut carrying instruments hanging from a bar. The instruments had
an Earth-weight of 190 pounds, supposedly 31 pounds on the Moon, but the
pronounced bowing of the bar would not have been caused by just 30
pounds.
During the early Moon trips, the astronauts stated that when they left
the atmosphere, the stars were not visible. This is understandable as
the atmosphere scatters starlight, making stars appear larger and so
become visible to the naked eye. Outside the atmosphere, there is no
scattering and the stars are too small to be seen without a telescope.
On the Apollo 11 trip, shortly before reaching the Moon, Collins stated
“Now we’re able to see starts again and recognise constellations for the
first time on the trip. The sky’s full of stars ... it looks like it’s
night side on Earth”. This demonstrates that the Moon has a
significant atmosphere caused by much higher gravity than one sixth that
of Earth, although the refraction of light through that atmosphere is
less than the refraction caused by Earth’s atmosphere.
Mr Cater points out that NASA is well aware of the real nature of
gravity and had electrogravitic drives long before the 1969 Moon shot.
Not only that, but due to the fact that the Moon is bigger than
currently believed, further away and possessing a higher surface
gravity, that rocket power used during the flight was supplemented by an
electrogravitic drive. Any honest person who has studied the evidence
is well aware that there are many craft with electrogravitic drives and
most of these seen in the last sixty years, are man-made. (All
governments are very keen to suppress this information as national
boundaries could not be maintained if electrogravitic drive vehicles
were available to the public).
2. Relativity, proposed by Albert Einstein, is not correct and Mr
Cater spends quite some time demonstrating that relativity is wrong.
Prior to Einstein, the Transverse Wave Theory of light was universally
accepted. Waves cannot exist without a medium which vibrates in some
manner to transmit them. Therefore, the “ether” which permeates all of
the universe was accepted. The Michelson-Morley experiment was set up
to test this. A ray of light was split into two parts which were made
to traverse different paths of equal length. The motion of the Earth
through the ether should then cause the recombined rays to show
diffraction patterns. They didn’t. It did not occur to anyone that if
light were retarded by passing through the ether, then bodies such as
planets would be seriously retarded by their passage through it and
would slow down and stop. This experiment also gave rise to the
ridiculous idea that the speed of light is a constant, in spite of the
well-known fact that the speed of light through water is only 75% the
speed of light through space. It was also proposed that the speed and
direction of movement of an observer didn’t matter, That time slows down
on a moving system, that a body will shorten in the direction of motion
and that the mass of a body will increase the faster that body moves.
These are ridiculous suggestions. The famous equation E = mC2was actually derived from the Lorentz equations in 1903, two years before Einstein got into the act.
Physicists argue that particle accelerators demonstrate the increase of
mass with speed. This is not the case and the experiments actually
demonstrate a very important principle which provides a better
understanding of many physical phenomena. It is an established fact
that a magnetic field develops around a charged body when it is given a
velocity. Where did the magnetic field come from? In the particle
accelerator, as the particles accelerated, magnetic fields developed
around them. As the total energy of the system remains constant, the
magnetic field must have developed at the expense of the electrostatic
field - the transformation of one kind of energy into another kind.
This conversion from repelling electrostatic charges to magnetic fields
causes the particles to clump together, giving the false impression of
an increase in mass. Further, as the electrostatic component drops to
almost zero, the accelerating force diminishes to near zero also, giving
the false impression that a material body can’t travel faster than the
speed of light. The reality is that bodies can travel many times the
speed of light.
According to General Relativity, a gravitational field will tend to slow
the passage of time and the stronger the gravitational field, the more
marked the effect. It was found that Caesium clocks run faster at high
elevations than they do at ground level. This has been taken as a proof
of the validity of Einstein’s ideas. The concentration of soft
particles is higher near the ground than at high elevations and that
makes clocks run faster at high elevations. As to the speed of light
not depending on the velocity of it’s source, the Sagnac experiment of
1913 provides direct proof that the observed velocity of light is
dependent on the velocity of it’s source, disproving Relativity. Mr
Cater provides extensive demonstrations (as do other people) that
Einstein’s deductions are not correct.
3. It is clear that gravity is responsible for the tides, but the
standard explanation is wholly inadequate, being based on the
assumption that gravitational effects have unlimited penetration. In
other words, the only attenuation when passing through matter is due to
the inverse square law, which actually would be a violation of the law
of conservation of energy.
It is well known that a body cannot be given an acceleration relative to
another body if both bodies experience the same acceleration. It
follows then that since large bodies of water are accelerated relative
to the Earth to cause tides, the water is being experiencing a different
acceleration than the Earth as a whole, otherwise, there would be no
tidal movement of water across the surface of the Earth. Assuming that
gravity has unlimited penetration causes problems when accounting for
tidal movements. Since the distances between the Sun and the Earth and
the Moon and the Earth are large in comparison to the diameter of the
Earth, all parts of the Earth will experience nearly the same
gravitational attraction from these external bodies if gravity has
unlimited penetration. High tides tend to occur when the Moon is at
it’s zenith, both directly underneath the Moon and simultaneously, on the opposite side of the Earth.
The Earth’s orbit is inclined to the Equator by 28 degrees and so the
Moon is never further North or South than 28 degrees. According to
Newton’s theory, the highest tides should occur near the Equator but the
reality is that the highest tides are experienced much further away
from the Equator, both North and South of it. Mr Cater provides an
in-depth discussion of these effects, demonstrating that Newton’s
concept of gravity is wrong.
4. It is generally accepted that energy, in any form, flows from a
higher potential to a lower one. The law of redistribution of energy
states that when radiant electromagnetic energy interacts with matter,
the resulting radiation as a whole, is of a lower frequency than the
original light. This is why temperatures at lower elevations are
generally higher than those at higher elevations, as sunlight passing
through air converts to lower frequencies including infrared which
activates the thermal motion of atoms and molecules, thus producing
heat. Any dynamic unit is less active as a whole, than the individual
parts comprising it. The higher ethers consist of the smaller, more
active particles while the lower ethers are composed of the large, more
complex and consequently less active particles. Both ethers occupy the
same 3-dimensional space (which is the only space that there is).
When light of a given frequency range is produced, only the ethers
associated with this light are directly activated. Light photons are
composed of combinations of ether particles. Photons combine to form
the penetrating particles which accompany this light. Particles
composed of light in the lower frequency ranges are referred to as
“soft” particles while those associated with gamma rays and above are
referred to as “hard” particles.
Soft particles are more penetrating than the photons from which they are
made, because, unlike the larger soft particles, photons have a
relatively great surface area in proportion to their mass. Soft
particles, and particularly soft electrons, play a vital role in all
life processes and in other chemical reactions. The energy or field
intensity of and around the higher ether particles is greater than that
of the lower ethers. The diameter of a particle is inversely
proportional to the average frequency of it’s constituent light.
5. The energies radiated from the Sun are continuously
transformed into ever lower frequencies as they penetrate into the
Earth. In this manner, nearly all of the original ultraviolet is
transformed into lower frequency radiation by the time it penetrates the
shell of the Earth. It is the transformation of some of the radiation
from the Sun into gravity-inducing radiation which holds the Earth and
the other planets in orbit around the Sun and give the illusion that the
Sun has about thirty times Earth gravity. It should be mentioned that
soft particles penetrate solid matter more readily than hard particles
which are, of course, an integral part of matter.
All matter continuously radiates soft particles of many different kinds
due to the interactions of the fundamental particles. These radiated
particles undergo a transformation effect, according to the
transformation law, when passing through large concentrations of matter.
When this occurs, some of the radiation is transformed into
gravity-inducing radiation. This is the source of some of the surface
gravity of both the Earth and the Moon. The greatest contributing
factor to Earth and Moon gravity is the transformation of radiation
resulting from the thermal agitation of atoms and molecules. The
particles resulting from this activity are comprised of lower-frequency
photons. Such radiation is more readily transformed into
gravity-inducing radiation because it is closer to this frequency band
to begin with. A significant portion of this radiation, originating
miles below the surface, is converted into gravity-producing energies by
the time it reaches the surface. Most of the gravity radiation of the
Earth and the Moon is created in the topmost fifty miles of their
crusts. Below that level, much of the energy from the Sun has been
transformed into softer particles, and that material of the Earth and
Moon is permeated with them.
These soft particles screen out gravity radiation more effectively than
solid matter does. This is because the ethers with which they are
associated, are closer in frequency to the gravity radiation band. This
explains why Moon gravity is nearly equal to Earth gravity. At the
same time, it is clear why the Cavendish Experiment for determining the
so-called “gravitational constant” was misleading – there wasn’t enough
material in the bodies used in the experiment to produce any radiation
transformation. The gravitational effects produced by the bodies were
due entirely to the thermal agitation of the molecules, without any
transformation of radiation. The thermal agitation of molecules
produces infrared and only an infinitesimal portion of this radiation is
in the gravity-producing frequency range. This “gravity constant” plus
the idea of unlimited gravity penetration, requires scientists to
assume that the Earth has a tremendous mass and an iron core four
thousand miles in diameter.
It is significant that some of the Cavendish Experiments indicated that
gravity effects varied with the temperature. When the large sphere used
ion the experiments was heated, the smaller sphere had a greater
tendency to move towards the larger sphere. When the larger sphere was
cooled, the smaller sphere receded. This was explained away as being
caused by convection currents although they failed to explain how
convection currents could produce such an effect. A detailed account of
this can be found in the 11th edition of the Encyclopaedia Britannica
in the section entitled “Gravity”. (If they felt that air currents were
skewing the results, then the experiment should have been repeated
inside a box which had the air removed).
As mentioned before, matter produces infrared radiations which are
partially transformed into gravity radiations. In the case of mountain
ranges, there is not enough matter to transform significant portions of
such radiations into gravity radiations. Much of the radiation will
escape from the tops and slopes of the mountains before they can be
transformed, since their average heights are generally small compared to
their horizontal dimensions. The gravity radiations produced deep in
the interior of the mountains are partially dispersed by the overlying
mass. This is the cause of the plum bob enigma which is a source of
annoyance to conventional physicists because the plumb bob is not pulled
towards the mountains to the extent demanded by Newtonian laws.
Another problem is that, in comparison to the Sun, the Earth radiates
only an infinitesimal amount of radiation per unit of surface area but
it is able to keep the Moon in it’s orbit around the Earth. Even
allowing for infrared radiation passing from the Earth to the Moon and
converting to additional gravitational radiation there, it still
wouldn’t be enough to keep the Moon in orbit unless the Moon were hollow
and had a shell not more than a hundred miles thick.
In 1978, scientists were shocked to discover that some of the asteroids
have moons which orbit around them at respectable velocities. According
to Newton, this is impossible as the gravity of an asteroid would be
far too feeble to allow this. When a body is a few miles across, it is
large enough for gravitational radiation to be produced. This effect
increases rapidly as the size of the body increases as far more infrared
is transformed than is screened out by the outer layers of the mass.
The effect continues until the body is about 150 miles in diameter and
beyond that point, the screening effect of the outer layers keeps pace
with the rate of increase of the transformation of infrared into gravity
radiation. This means that all planets have practically the same
surface gravity.
6. Mr Cater explains how soft and hard particles and the limited
penetration of gravity account for Erath upheavals, continental drift,
earthquakes and volcanoes. He also remarks that if the Earth were a
completely solid ball and the Newtonian version of gravity were correct,
then the Earth would be completely rigid and no Earth changes would
occur other than some minor erosion, and there would certainly be no
mountains left by now.
7. One of the most fundamental physical laws involves the
relationship between the electrostatic and magnetic fields. One
transforms into the other and vice versa. Inertia is a third factor
involved in the relationship between the electrostatic and magnetic
fields. The kinetic energy of a moving charge is manifested in it’s
magnetic field. The magnetic field increases at the expense of it’s
electrostatic field (as dictated by the law of conservation of energy).
The role of inertia and the conditions governing it’s magnitude are now
apparent. The inertia of a body is dependent on it’s ability to
generate a magnetic field when it is given a velocity. The greater the
inertia, the greater this ability.
The magnitude of the inertia of a body is directly proportional to the
energy of the magnetic field which the body develops for a given
increase in velocity. It follows then that inertia is dependent on the
total electrostatic charge of a body. This is also true for so-called
“uncharged” matter. In the supposedly uncharged state, all atoms and
molecules have a net positive charge. Therefore, even atoms and
molecules develop a magnetic field when they are given a velocity.
In 1901, Max Planck found that he could only derive the correct
distribution in frequency of the radiant energy in the cavity of a black
body as a function of the temperature of that body, if he assumed that
energy exists in discrete units. He came up with NHV where N is an
integer, V is the frequency of the light involved and H is a universal
constant (expressed in terms of energy multiplied by time, that is,
erg-seconds). This is now known as Planck’s Constant and is 6.6 x 10-27
erg-seconds.
The kinetic energy of a light photon is inversely proportional to the
frequency. The lower frequency light, consists of larger and more
massive photons travelling at the same velocity as the higher frequency
photons. On average, the number of photons in any given ray, and the
number of accompanying soft electrons will be a constant, regardless of
the frequency. This is in accordance with the conclusion that the
average distance, or mean free path between ether particles of the same
kind, is a constant, regardless of the ethers involved. The average
number of photons comprising a soft electron will also be independent of
the frequency. This means that the diameter of the surface area of a
soft electron, will also be inversely proportional to the frequency.
Soft electrons accompanying light, travel at a velocity which is less
than that of light. The soft electrons pick up speed, by bombardments
of faster moving photons.
From a superficial glance, it seems that the average velocity of soft
electrons should be independent of the frequency of the light associated
with them. This is not so. The soft electrons associated with the
higher frequency, travel at a higher velocity, and herein lies the key
to the photo-electric effect. Although the lower mass of the higher
frequency soft electrons is offset by the lower kinetic energy of the
bombarding higher frequency photons, the surface area is greater in
proportion to mass. This means that in proportion to mass, the
electrons associated with the higher frequency light will receive a
greater bombardment of photons and so, a greater accelerating force.
The ratio between surface area and volume, or mass, is inversely
proportional to the ratio between the diameter of two given spheres.
Since the other factors balance out, it follows that the resultant
average kinetic energy of soft electrons in proportion to mass, is
directly proportional to the frequency of the light with which they are
associated. As soft electrons collide with a surface, the hard
electrons which they contain, are released and they bombard the surface,
producing the photo-electric effect. They will be travelling at the
same velocity as the soft electrons which housed them, so their average
kinetic energy will be proportional the frequency of light.
Quantum mechanics is considered the most monumental achievement of
twentieth centaury physics. In view of the principles presented above,
it is not surprising that mathematical juggling with Planck’s constant
would account for many experimental results (in a quantative sense).
Quantum mechanics experts have enjoyed considerable success in this
respect, especially in the realm of atomic spectra, without knowing why.
In reality, quantum mechanics does not even qualify as a theory or a
concept. It is merely an attempt to give mathematical descriptions of
certain phenomena with Planck’s constant and his valid assumption as a
starting point. Modern “theoretical” physicists have absolutely no
conception of why their mathematics agrees with certain experimental
results. Yet, they have led themselves to believe that by giving
mathematical descriptions of such phenomena, they have actually
explained them.
It now becomes evident, why a mass can travel through space at a
constant velocity, and encounter no decelerating force. The ether
particles are so active that the closing forces at the back of the
moving body, tend to equal the resistive forces encountered at the
front. The rear portion creates a temporary void which is rapidly
filled in by the surrounding ether particles, producing an effect very
much like the Coander Effect. During the filling in process, the
fundamental particles comprising the rear of the body are bombarded with
ether particles travelling at a higher velocity than is normal. Also,
the ether particles of which the mass is comprised are so relatively
sparsely distributed throughout space, the situation is equivalent to a
great mass travelling through a highly rarefied atmosphere.
8. During the creation of a photon, the ethers in the vicinity
are suddenly compressed. Some of the ether particles are forced close
enough together to adhere to each other. This aggregate is then
propelled outwards with great force in a manner similar to a compressed
spring being released. The photon reaches the speed of light after this
accelerating force has been expended, which happens in a distance equal
to the so-called wavelength. This process is repeated in the same
region and another photon is produced which follows the first one, just
one wavelength behind. A wide range of ethers are periodically affected
during the production of ordinary light. This results in a countless
variety of such particles being propagated in all directions with many
different wavelengths. Since many photons are projected in all
directions, many collisions will result, causing a significant portion
to adhere to each other in aggregates.
The great majority of soft electrons are created during fluctuations in
light velocity when passing through media of varying density, and even
in it’s passage through outer space. Any slowing down, produces a
backing up of photons and a consequent combining into relatively huge
aggregates. In the beginning, these aggregates move much more slowly
than the free photons. Consequently, some of the photons which were
created at a later time, catch up and adhere to the aggregate. Their
collisions with the aggregate particles causes the particles to speed
up. This is the origin of the particles which always accompany light.
Particles formed in this manner will vary greatly in size, stability and
penetrating ability. It has been shown that soft particles will
penetrate ordinary matter more readily than the hard particles. So,
ether particles combine to form photons which in turn, combine to form
light particles. This, light particles will disintegrate into photons.
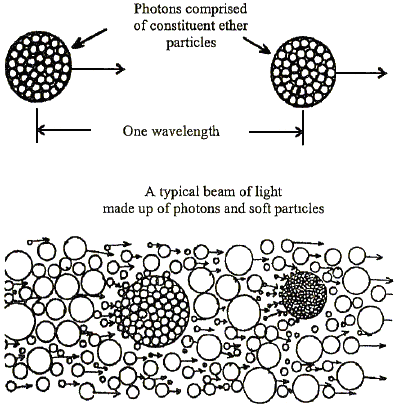
Atoms are comprised of hard particles which are uniform in size and structure and it follows that they were produced by an entirely different process. When light enters a medium, it encounters a conglomerate of soft particles created by the activities of the fundamental particles of the atoms which comprise the medium. This causes the light to slow down and the particles of light to crowd together inside the medium. If a beam of light enters a medium at an angle, the portion entering first will travel a shorter distance than the rest of the beam during the same interval of time. The portion of the beam entering the medium later is pulled by magnetic attraction of the particles, towards the side which reached the surface first. This causes the beam of light to be bent or change direction, accounting for the refraction of light which has never before been adequately explained.
Mr Cater then goes on to resolve the famous wave-particle paradox, and the also points out that the famous Michelson-Morley Experiments actually disprove the Transverse Wave Theory of light.
9. It must be realised that nature’s laws are basically simple. To gain a deeper understanding of the nature of electrons, protons and electrostatic forces, it is necessary to look for an uncomplicated picture of the fundamental particles and the cause of their behaviour patterns. The collision laws involving the molecules of a gas can be applied to the ethers. Also, it can be deducted that electrostatic forces are the result of an imbalance of ether particles bombarding fundamental particles of matter.
It seems logical to assume that electrons and protons have a spherical shape as a sphere is the most stable and efficient geometrical form. It also has the smallest surface area for any given volume. However, such an assumption leads to insurmountable difficulties. Electrons and protons have a preferred direction of spin in relation to their direction of motion. The electron follows the left hand rule, while the proton spins according to the right hand rule. With a perfect spherical shape they could not have any preferred direction of spin. However, the preferred directions of spin can be readily accounted for if the particles are pear-shaped or egg-shaped and they are hollow.
When ether particles have a preferred direction of motion away from the electrons due to reflections, a pulsating electric field results. The excessive flow away from the electron tends to reduce the bombardment of incoming ether particles. A temporary low ether pressure around the particle is a result of this and in turn, this reduced pressure reduces the reflections and that causes the ethers to move in again and a sudden increase in ether bombardment results. This is something akin to the Coander Effect. The cycle is then repeated. It is to be expected that an electrostatic field is no exception and in this respect, “electrostatic” is a misnomer. The fluctuations are at such a high frequency that experimental results will see the (average) force as being a constant.
The behaviour of beams of electrons and protons in strong magnetic and electric fields indicates that protons have about 1836 times the inertial mass of electrons. Inertia is directly proportional to charge, indicating that the total charge of a proton is 1836 times as great as that of an electron. The idea that the hydrogen atom consists of one electron and one proton has never been questioned. To quote from a science magazine: “When protons crash into each other, they release showers of electrons, which suggests that protons are made up of particles more basic than themselves”.
On the basis of relative charge effects alone, it follows that a hydrogen atom, instead of having only one electron orbiting a proton, that there are at least 1836 orbiting electrons. However, since the proton has relatively little movement in comparison to the electron, a far greater percentage of the electrostatic field of the electron has been transformed. This means that in order for the hydrogen atom to have close to a neutral charge, there must be thousands of electrons in one hydrogen atom. This seems to create a paradox as the amount of electricity required to liberate a given amount of hydrogen in electrolysis indicates that only one electron is necessary for every atom of hydrogen.
Scientists have never comprehended the source of the electricity that powers electrical equipment. There are unlimited quantities all around us, permeating all of known space. This hard electricity is camouflaged by softer particles which are also distributed throughout space. The flow of this limitless source of electrons can easily be set into motion. The electricity employed in electrolysis merely triggers the flow of far greater quantities. Also, when a hydrogen atom is ionised, it only needs to lose a very small percentage of it’s electrons instead of being reduced to only a proton.
Matter is rendered visible by the steady formation of soft particles generated by the activities of the fundamental particles. It is then apparent that frozen hydrogen would be completely invisible if electrostatic fields were not cyclic and the hydrogen atom had only one electron. Cyclic electrostatic fields are largely responsible for the complex spectral pattern of all of the elements. The cyclic pattern of hard-particle interactions is complex. This complexity increases rapidly as the number of fundamental particles in the atom increases.
Since electrons move at much higher velocities in the atom than protons do, they cover much more territory and so a higher percentage of their electrostatic charge is transformed into magnetic energy. This means that the positive charge in the atom will overbalance the negative charge and so, give the atom an overall positive charge. This explains why electricity tends to move towards ground and the Earth must posses a positive charge.
The electrostatic field effects near the atom in close proximity to the electrons, will be negative. Moving outwards, this negative effect diminishes quickly and a zone of positive field effect exists. The position and intensity of these zones, determines in part, the chemical and physical properties of the atom. There are regions where the atoms will attract each other and regions where they will repel each other. Ether particles have a similar structure and follow the same pattern.
The velocity of orbiting electrons in atoms is not uniform. There are periodic fluctuations resulting from mutual interferences within the atom itself and from adjacent atoms, in addition to the pulsating electrostatic fields. It must be noted that the properties of the atom are not observed individually, but as a collective group. The region of activity for the protons is relatively small and a significant number of electrons are trapped here. This region is the origin of neutrons, which are actually collapsed hydrogen atoms. It is interesting to note that when hydrogen is subjected to ultra high pressures, it behaves like a high concentration of neutrons and passes through the container which is being pressurised as though it didn’t exist.
A more detailed discussion of the structure of the neutron is in order. The new concept of thousands of electrons comprising the hydrogen atom (to say nothing of the other atoms), provides, for the first time, a means of accounting for the properties of the neutron.
When a cloud of electrons orbiting the proton is forced into close proximity with the zone of repulsion, as described earlier, their motions become restricted. As a result, there is a lowering of the average velocity with a consequent increase in their negative electrostatic charge. This provides a stronger bond between the proton and the electrons. The orbital speed cannot be increased because of the zone of repulsion surrounding the proton, and the crowding of the electrons. The higher overall negative charge of the electrons almost completely cancels out the positive charge of the proton. The result is a particle which is electrically neutral, as far as most experiments can determine.
The electron cloud comprising the hydrogen atom is further removed from the proton and the individual electrons are not restricted in their orbital motions. The average velocity is much higher and consequently, the hydrogen atom has a high positive charge. The atoms of the gaseous elements, such as hydrogen and oxygen, are highly magnetic. Therefore, two atoms combine in much the same way as two bar magnets, to form a molecule consisting of two atoms. This is the reason why the molecules of nearly all the gaseous elements consist of two atoms. The combination has a still higher overall positive charge than a single atom has. As a result of this, the molecules have a strong mutual repulsion which keeps them widely separated at normal temperatures and pressures. Thus, they remain a gas even at extremely low temperatures.
The presence of electrons in the “nucleus”, nullifying repulsive forces, along with the magnetic fields resulting from the motions of neutrons, is the major source of the so-called “mysterious force holding the nucleus together”. In reality, the pinch effect of magnetic fields is the prime force which holds the atom together. Orthodox physicists have complicated the picture by claiming that many different forces exist: magnetic, electrostatic, gravitational, nuclear, and others to which they have ascribed odd names. In reality, only electrostatic and magnetic forces exist and there are two, and only two, basic particles – electrons and protons. Since the electrostatic field effects around the electron and proton are cyclic, the magnetic fields which they generate will also have a cyclic intensity.
10. Although neither spin when at rest, both the electron and the proton start to spin in a definite direction when they are given a velocity. This is contrary to the assertions of modern theorists who talk about particle spin with reckless abandon. The electron always follows the left-hand rule, while the proton follows the right-hand rule.
When placed in an electrostatic field, they move in such a manner that the large end is facing in the direction of their motion, regardless of their original orientation. The reason for this is not difficult to discern. If they are hollow and the shell is of a certain thickness in proportion to it’s diameter, then the larger end will have more surface area in proportion to it’s mass than the smaller end will have. The thickness of the shell at the smaller end will be much greater in proportion to it’s diameter. This means that ether bombardment at the larger end will tend to give it a greater acceleration than that imparted to the smaller end and as a result, the larger end will be forced ahead in the direction of motion.
The picture is still incomplete. In order for the particle to have a preferred direction of spin, the frontal surface must be grooved in the manner of a right-hand or left-hand screw. Such a shape is consistent with recent experiments at the Argonne National Laboratory, which studied the shattering of proton beams aimed at target protons. The results indicated that protons are not spherical. A detailed account of such experiments can be found in the article “The Argonne Experiments and The End of Quarkery” by Eric Lerner which appeared in the Oct-Nov 1997 issue of Fusion Magazine. In the article he showed that some of the basic assumptions of quantum mechanics are contradictory, and he dispensed with the popular theory in particle physics which assumed an ever-growing family of hypothetical particles called “quarks”.
It has been noted that a magnetic field surrounds a moving charge. The magnetic lines are in the form of circles. An electron or proton tends to carry ether particles around with it in a circular motion as it moves through the ethers. This is due to the mutual repulsion between the ether particles and the ether particles comprising the particle. The reactive forces cause the particle to spin and they produce a vortex motion in the ether itself. The greater the velocity of the particle, the faster it spins and the more ether particles are caused to flow around it in the direction of the spin. It is this flow of ether particles around a moving charge which produces the magnetic field effects observed. A three-dimensional view of this magnetic field shows that it resembles a corkscrew spiral or vortex.
The ether particles which would normally cause repulsion between two adjacent particles at rest, spin when they both move and the electrostatic repulsion drops off and is replaced by a magnetic field which draws the two particles together. This effect is also seen in two adjacent wires carrying a heavy current flowing in the same direction. The wires are drawn towards each other.
If two unlike charges move along together, they spin in opposite directions, generating magnetic fields of opposing polarity which tends to push the particles apart.
An electron or proton moving in a magnetic field has two forces acting on it. One force tends to push it down the magnetic lines of force because of excessive ether particle bombardments in one direction of flow. The other force is perpendicular to the lines of force. If the velocity of the particle is high, then the latter force is by far the more significant. This force is a result of Bernoulli’s principle. Magnetic fields tend to capture large quantities of soft electrons.
11. The conventional theory of geomagnetism lacks merit. According to it, the major portion of geomagnetism is the result of electric currents flowing in a molten iron core 2,000 miles beneath the surface of the Earth. Even if such a core did exist, the conclusion would still be false. Scientists are somewhat vague as to how a magnetic field could extend 2,000 miles beyond an electric current considering that it takes a very powerful current to produce even weak magnetic effects a short distance from the current flow. The electrical resistance of iron at the alleged temperatures of the core would be staggering, which raises the question of how the necessary massive potential difference is produced to drive a large current in the core in the first place.
A great wealth of evidence supports the conclusion that geomagnetism is produced by the Earth’s rotation. The intensity of the field is dependent on the concentration of negative charges in the atmosphere and the crust and on the rotational velocity. Since the concentration of charges in the atmosphere fluctuates in a 24-hour cycle, the magnetic field can be expected to fluctuate accordingly. This is an established fact.
Supposedly uncharged atoms and molecules are not electrically neutral, but possess a positive charge. It has always been assumed since the days of Newton, that inertia is directly proportional to mass. This has been shown to be incorrect as inertia is dependent on total charge and is therefore independent of mass. It follows that an atom has less inertia than any of the fundamental particles of which it is composed. The small overall charge of an atom is the result of the equalising of positive and negative charges. It’s slight ability to generate a magnetic field for a unit increase of velocity is due to electrons following the left-hand rule while protons follow the right-hand rule. The inertia of an atom is limited because the magnetic fields of the electrons and protons from which it is constructed, cancel each other out to a major degree. Stripping electrons from an atom will give it a strong positive charge and much greater inertia even though it now has less mass. Adding electrons to it can also raise it’s inertia if the extra electrons cause it to end up with a greater overall charge than it had before. The Nobel Prize winner Gabriel Lippman confirmed this when he found that bodies in a charged state have greater resistance to acceleration than they have in their uncharged state.
Since matter behaves like a positive charge, it follows that gravity radiation will accelerate positive charges in a direction opposite to that of the direction of its propagation. A gravitational field repels negative charges. When the hair on a person’s head is given a strong negative charge, it stands straight up due to the negative charges on the hairs carrying the hairs with them as the charges are pushed upwards by gravity.
The bulk of the radiations and soft particles of matter cover only a relatively narrow part of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are produced by the interactions of the fundamental particles of the atom in addition to the interactions of the atoms themselves. Incidentally, it is the soft particles comprised of photons close to, and in, the visible range which permeate matter that make matter visible. If only the hard particles were present, solid matter would be invisible, although completely tangible.
The leading part of the gravity radiation front produces negative charge effects, while the trailing portion which has passed a given body must have substantially reduced negative charge effects. The spin of the particles in gravitational radiation have a gyroscopic effect which keeps the particles orientated in the same position and the particles have little tendency to scatter.
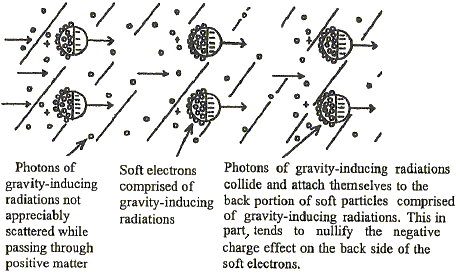
The faster moving photons overtake the soft particles and tend to adhere
to them in irregular patterns, creating a perforated and extremely
rough surface on this part of the particle, not unlike that of a
positive charge. This has a tendency to cancel out much of the negative
field effects on this part of the particle. The bombardments
accelerate the particles to such an extent that no more photons can
adhere to them. Therefore, the rear part maintains a positive charge,
or at least, a much reduced negative charge.
Another important factor which contributes to a reduced negative charge
at the rear is that there is a far greater photon concentration in this
region than exists at the frontal portion. This is a result of a backup
of photons caused by the lower velocity of the soft particles
accompanying the radiation. This photon concentration tends to divert
the normal ether bombardments (which produce the electrostatic effects)
from their usual paths. Since gravity radiations produce forces, it
follows that there are interactions which eventually disperse the
radiation, accounting for the limited penetration of gravity radiation.
Gravity is an electrostatic effect, not some space warp or mysterious
force with imponderable properties. If matter is impregnated with
sufficient quantities of negative charges, especially soft electrons, it
will become weightless and even levitate.
Some individuals have the ability to do the reverse of levitation,
possibly by expelling large quantities of negative charge from their
bodies. A dwarf who had a normal body weight of 123 pounds demonstrated
under strict anti-fraud conditions that he could increase his weight to
900 pounds.
The physics of levitation was demonstrated in part when missiles were
found to have lost most of their original weight after travelling
through the Van Allen Radiation Belt and returning to Earth. The weight
loss continued for some time and containers in which pieces of the
missile were placed, also lost weight. The radiation belt contains high
concentrations of negative charges of all kinds, from hard electrons to
the very soft ones. The missile became impregnated with negative
charges as it passed through this region, absorbing an abnormal
quantity. The more penetrating softer particles opened the door for the
harder particles to enter. The loss of weight of the container would
have been caused by the missile gradually losing some of it’s excess
negative charges and those charges being absorbed into the container.
12. Faster than light travel is possible because the accelerating
gravity beam travels with the mass being accelerated. At ultra-high
velocities, or where most of the electrostatic potential of matter has
been transformed, cohesive forces will tend to break down and the
material will cease to be a cohesive solid. However, spaceships can
travel many times the speed of light provided that the ship and the
occupants are impregnated with the right combination of negative charges
which would prevent any extensive transformation of the electrostatic
mass into magnetic energy. At ultra-high velocities, the closing forces
on the rear of the craft no longer compensate for the forward
resistance, so it requires a steady application of accelerating forces
to maintain velocities many times that of light.
The evidence concerning spaceship propulsion demonstrates that the famous Einsteinian equation E = mC2 falls far short of representing the energy potential of matter. From the kinetic energy equation E = 0.5mV2 it follows that a body travelling at only 1.5 times the speed of light
(which isn’t even a cruising speed for most spaceships) has a kinetic
energy which exceeds the value of Einstein’s celebrated equation. At
this velocity, only a miniscule part of the energy potential of the mass
has been released. The meaninglessness of the famous equation is also
evident, because inertia is dependent only on net charge and not
necessarily on mass or quantity of material.
13. Another item which demonstrates the validity of the
information presented here is the fact that determinations of the
gravity “constant” “g” is always significantly higher when measured in
mines. This is to be expected as the soft electron concentration is
much higher below the surface than it is above the surface. Another
fact which disturbs physicists (and consequently given little publicity)
is that objects at the bottom of mine shafts weight significantly less
than they should according to Newton’s concept of gravity.
Another enigma which is damaging to the academic viewpoint is that
experiments indicate that gravity doesn’t impart the same acceleration
to all substances. To try to deal with this fact, they have to
introduce a mysterious fifth force which is supposed to be an extremely
feeble repulsive force with a limited range. It is supposed to be more
prevalent in some substances than in others. The concepts already
explained here show that this is to be expected. Different atoms and
molecules have different total positive charge effects in proportion to
the number of fundamental particles from which they are made.
Consequently, they will not be given the same gravitational acceleration
even if the mass is identical.
14. We now come to questions such as; How does the law of
redistribution of energy work? What are the real principles behind
colour perception? Why is the velocity of light independent of it’s
frequency? Why is this velocity equal to the ratio between an
electromagnetic and electrostatic unit of charge? The answers to these
questions have never been given before.
When materials are subjected to high temperatures, great fluctuations
occur in the velocity of electrons in their orbits. This in turn,
creates interactions and interference effects between electrons moving
in opposite directions inside atoms and between electrons in adjacent
atoms. These interactions generate changes in the electrostatic field
effects of the electrons, which will cause regular and distinct changes
in their so-called orbits. This is because the charge on the electron
varies with it’s velocity. Abrupt changes in the velocity of a particle
disrupt the ethers which results in the formation of photons.
The larger the atoms, the more complex the interactions, and
consequently, the more intricate the spectral pattern. The photons
comprising the electrons, determine the range of the ethers which will
be disrupted. These ethers are intimately connected with the
electrostatic field intensity of the electrons. Thus it follows from
this new definition of Planck’s constant, just why this definition must
be taken into consideration in all of the calculations concerning the
frequency of light produced in interactions.
The electrostatic field effects around an electron depend on the range
and level of the ethers deflecting off the sides of the particles. This
range is not necessarily the same as the range of ethers affected by
sudden changes in the velocity of the electrons, but there is a direct
correlation between the two. Planck’s constant has a role throughout
the procedure as all ether particles have the same kinetic energy.
The law of redistribution of energy states that when light interacts
with matter, new light with a lower average frequency than the original
is produced. One of the most simple demonstrations of this is shining a
blue or violet light through a large number of filters of any type.
The emerging light is always red. All of the colours which we normally
see are combinations of different frequencies of photons. A wide
frequency range of soft particles and photons will tend to be grouped
together. This means that bands of light in the blue, indigo and violet
ranges will contain other colours down to the reds, although the reds
will make up only a very small percentage. The human eye sees only the
dominant colour, and prisms cannot separate them. The colour
experiments of Edwin Land proved this to be the case.
In the May 1959 issue of Scientific American, Land showed that
two black and white transparencies produced from black and white film,
were exposed to filtered light from two different (reasonably spaced
apart) parts of the spectrum, the resulting superimposed images were in
full colour. This shows that it requires subtle combinations of
frequencies for the eye to perceive colour if the light isn’t in a
narrow frequency band. Otherwise, the eye will see things in various
shades of black and white, which contain all the colours but in the
wrong combinations to be seen as colours. This is what occurs for
people who are subject to ‘colour blindness’.
Under certain conditions, light reflected from a mirror can have greater
intensity than the incoming light. The light has to be of high
intensity. When the particles of the incoming light collide with the
mirror, those that are reflected are instantly brought to a halt. This
produces a tremendous disturbance of the ethers which results in the
creation of new photons which are added to the photons which are
reflected. In addition, many of the photons reflected and created,
combine to form soft electrons, and so the reflected light has a higher
percentage of soft electrons than the incoming light beam.
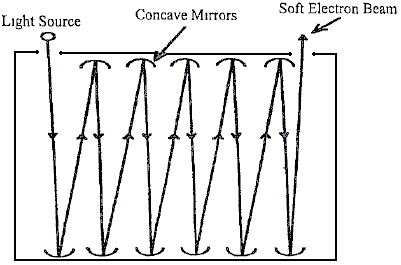
It follows that repeated reflections of a light source such as the Sun,
would result in a highly lethal laser-like beam. This has been
demonstrated on numerous occasions. Perhaps the most notable
demonstration occurred near White Sands, New Mexico in the early 1950s.
It was witnessed by an acquaintance of a personal friend of Mr Cater’s,
and it was something which he wasn’t supposed to have seen. About
thirty-five four foot diameter mirrors were arranged so that the
resulting beam was directed at the rock wall of a mountain. It
immediately created a neat hole through 200 feet of solid rock.
An associate of Mr Cater’s found that by putting a strong negative
charge on the mirrors that their reflective power is considerably
increased. He charged a series of metallic mirrors to 20,000 volts and
found that after 10 repeated reflections from the Sun, the resulting
beam was very lethal. This shows that it is the negative charges
deposited on a mirror surface which enables it to reflect most of the
light that falls on it. Incoming light immediately deposits negative
charges on the surface and those charges repel the rest of the light.
The more intense the incoming light, the higher the concentration of
negative charges placed on the surface. This accounts for the fact
that highly lethal beams reflecting from the surface do not destroy the
mirror. The mirrors must be metallic and preferably concave. Glass
mirrors do not work as much of the incoming light is lost before it
reaches the reflecting surface and much of the shock effect of the light
reflection is lost due to the glass slowing down the incoming beam.
The incoming light must strike the mirror in as nearly a perpendicular
direction as is possible. If soft electrons associated with colours
known to be highly beneficial could be concentrated using this method to
produce rapid healing
15. The question arises: Why is the velocity of light independent
of it’s frequency? This is implicit in Maxwell’s equations but it
still isn’t explained. When the ethers are disturbed to produce a
photon, a fraction of them are compressed and a great number are forced
close enough together to adhere to one another. The higher the ethers
affected, the more rapidly and suddenly this displacement has to occur
in order for a photon to be produced, otherwise, the ether particles
will escape this compression since they are very active. This momentary
compression quickly returns to normal, rather like a compressed spring
being released. This rebound hurls the aggregate photon forward at the
speed of light. The distance of this rebound is equal to the so-called
wavelength, or distance over which the photon is accelerated to the
speed of light.
This is exactly what happens when lower ethers are disturbed to form
lower frequency photons, except that the rebound takes place over a
greater distance with a lower average acceleration of the photon. Since
the warped pattern is identical in both cases, both photons reach the
same velocity, which is independent of the actual wavelength produced.
As both photons receive the same thrust, it can be seen that lower
frequency photons must have a greater mass, that is, the frequency of
light is inversely proportional to the mass of the protons which form
that light.
The behaviour of electrons and protons in a particle accelerator shows
that at the speed of light, all of their electrostatic potential has
been transformed into magnetic energy. This shows that the velocity of
light relative to it’s source is the ratio of it’s Electromagnetic Unit
of charge (“EMU”) and it’s Electrostatic Unit of charge (“ESU”). The
ratio EMU / ESU is equal to the speed of light “C”. Calculating from
these details, shows that the total pressure exerted on a single
electron by the surrounding ethers is 14.4 dynes which represents a
pressure beyond normal comprehension when the minute size of an electron
is considered.
16. We now need to consider the role of soft electrons in
promoting chemical changes and maintaining life. It has been repeatedly
confirmed that magnetic fields have considerable healing properties and
will stimulate plant growth. What has not been realised is that it is
not the magnetic fields themselves which are responsible for this
effect, but it is the soft electrons which they capture and concentrate.
One pole of a magnet has beneficial effects for certain ailments,
while the opposite pole is not as effective.
One of the most significant properties of soft electrons is their
ability to promote chemical changes. A change in a molecule is not
likely to take place without lessening the chemical bond or attraction
among it’s constituent atoms. Soft particles interpenetrating the
molecule will bring about this condition by carrying harder electrons in
with them, which in turn weakens this bonding by offsetting the
positive charge effects of the nucleus. Soft particles tend to
camouflage a variety of harder particles. This is a vitally important
property because in this manner, other atoms which are going to take
part in the chemical change, also have their zonal effects temporarily
altered so that they can come into more intimate contact during the
reaction. The soft particles tend to act as catalysts for the reacting
particles and the soft particles tend to get disintegrated in the
process, releasing additional energy which expedites the reaction and
allows the normally powerful electrostatic field effects within the atom
to return to their original state. The release of the hard electrons
contained within the soft particles which disintegrate is the source of
much of the heat produced during chemical reactions.
17. The properties of water: water is a universal catalyst
because of it’s unique ability to collect and concentrate an enormous
quantity of soft electrons of all kinds. This is the reason why water
has the highest specific heat of any know substance. The large amount
of energy contained in water in the form of soft particles, has been
demonstrated by experimenters on many occasions. For example, a number
of reports show internal combustion engines running with water as the
fuel. No reasonable explanation for this has been given as it appears
to be contrary to all the rules of chemistry. However, the
disintegration of the more unstable soft particles contained in the
water when subjected to compression and ignition inside the engine,
accounts for this seeming impossibility.
Water is a unique substance being comprised of two of the most
chemically active elements, both of which are gaseous elements. The
fact that three oxygen atoms can combine to form ozone, indicates that
the oxygen atom is extremely magnetic, indicating that a higher
percentage of it’s orbital electrons are moving in approximately the
same plane. This leaves fewer orbital electrons tending to offset the
positive charge of the nucleus and other portions of the atom.
Consequently, two side of the oxygen atom possess an inordinately strong
overall positive charge. When hydrogen atoms combine with an oxygen
atom, the electro9ns on the side of the hydrogen atoms adjacent to the
oxygen atom are brushed aside. This is on the segment of the oxygen
atom where most of the electrons of the oxygen atom are orbiting. The
normal flow of electrons around the proton of the hydrogen atom is
diverted to become a flow which encircles the oxygen atom and the outer
periphery of the hydrogen atoms. This results in a powerful magnetic
and electrostatic bond between the hydrogen atoms and the oxygen atom.
The electron flow around the hydrogen atoms is extremely rapid,
resulting in a very high overall positive charge on the hydrogen atoms.
As there is a very strong mutual repulsion between the hydrogen atoms,
they will line up on opposite side of the oxygen atom, giving water the
structure H-O-H. This molecule has strong and extensive positive zones,
so the attraction zone is a considerable distance from the molecules.
This is why the specific gravity of water is low, despite the strong
positive charge of the molecules.
The great affinity of water for soft electrons is now apparent. The
large positive zones between molecules are havens for soft electrons,
drawn there by the attenuated, but significant, attraction of the hard
electrons captured by the soft electrons. Although soft electrons are
large compared to hard electrons, they are still very small compared to
an atom. Therefore, the spaces between water molecules can harbour
large quantities of soft electrons, without them being bound to the
water molecules.
Perhaps the most baffling feature of water is that it expands when it
freezes. The high concentration of soft electrons greatly weakens the
forces of attraction and repulsion between the molecules. As a result,
the average kinetic energy of the molecules at the freezing point are
still sufficiently large to allow the molecules to move in and out of
the zones of attraction and repulsion, without being confined in the
attraction zone. The cooling must continue until the soft electron
concentration reaches the stage where the attractive forces become
strong enough to confine the molecules to the attractive zone. When
this occurs, the water becomes a solid. Since the attractive zone is an
inordinate distance from the molecules, the average distance between
molecules becomes greater than it was when the water was in a liquid
state. At the freezing point, the molecular activity is low enough to
permit soft electrons to enter or leave the substance without
disintegrating. In order for the water to be transformed from a solid
back into a liquid, the same quantity of soft electrons must be injected
into it as were removed when it changed from a liquid to a solid.
The melting and freezing temperatures of water vary considerably due to
the differing amounts of soft electrons contained in it. Another
unusual feature is that in cold weather, hot water pipes have a greater
tendency to freeze than cold water pipes do. This is because the
heating of the water drove off many of the soft electrons normally
contained in the water and due to the low temperature of the
surroundings, these soft electrons were not replaced, and as a
consequence, freezing to become a solid happens more easily.
One tends to think of colloids as ultra-small particles of solid matter.
However, molecules of water can adhere to each other to form
aggregates of water molecules, which are effectively, colloids as well.
Colloids have strong electrical properties as indicated by the fact
that they are not affected by gravity. The field zones around any such
colloidal group will be much stronger than that around a single water
molecule. Water with a high percentage of such colloidal groups can
capture a very large number of soft electrons which are beneficial to
health. Abnormal conditions in certain places can favour the formation
of water colloids and that can account for the healing properties of
water found in some places, such as Lourdes in France.
18. Hard particles can be captured by softer particles and this
is deeply involved in a wide range of phenomena, from the transmission
of heat and electricity, to the formation of clouds.
Ether particles have zones of attraction and repulsion. Since photons
are composed of ether particles, they will in turn, possess zones of
attraction and repulsion. In the case of ether particles, these zones
will be correspondingly smaller in proportion to the diameter of
photons. When protons combine to form electrons or protons, the same
zones are present between these particles. However, the zones of
attraction are minute when compared to the diameter of the electron or
proton, and like particles, seldom if ever get close enough together at
sufficiently low velocities for the attractive forces to become
effective.
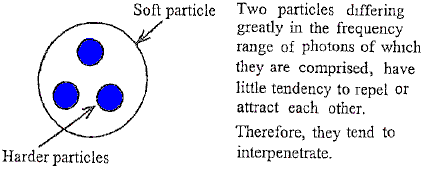
The situation is entirely different when two similar particles composed
of photons but with widely differing frequencies, approach each other.
Electrostatic attraction or repulsion is considerably lessened because
each is associated with ethers which differ considerably from each
other. When they are ion direct contact with each other, electrostatic
repulsion tends to vanish, since there can be little or no bombardments
on the sides facing each other. Since each particle associated with
ethers is somewhat different, they will tend to interpenetrate. This
means that they will be completely within the ether attraction zones of
one another. As a result, the harder particle is captured by the softer
one. In a similar manner, the captured harder particles will, in turn,
capture still harder particles and this process continues until
electrons normally associated with electricity are confined. This
combination of particles tends to nullify the electrostatic forces which
are normally produced by the confined particles, camouflaging the
captured harder particles so that their presence is not readily
apparent.
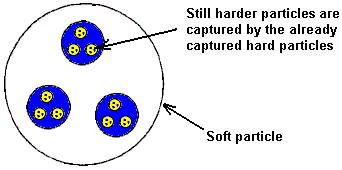
The ether particles normally bombarding the hard electrons and protons
which produce electrostatic field effects, tend to be diverted from
their normal paths by the presence of softer particles or media between
the repelling like charges and/or the attracting unlike charges. These
interpenetrating softer particles produce an ultra-high concentration of
ether particles around the hard particles. The motion of these ether
particles is greatly restricted. This offers a barrier to the higher
ether particles which normally bombard the hard particles. This has a
tendency to slow them down, and any which do collide with the hard
particles, do so with considerably less impact than normal, therefore
they tend to become electrically neutral and their motion slows to
nearly a halt.
Soft particles permeate matter as well as the spaces between matter, yet
they do not to any great extent, neutralise the electrostatic field
effects of the fundamental particles, because they are more concentrated
and their rapid motion tends to prevent capture. However, additional
concentrations of soft particles of the right kind, injected into
matter, can render the elementary particles within the atom,
electrically neutral and the matter becomes what is known as
“dematerialised”. This conglomeration of soft and hard particles
renders the soft particles electrically neutral.
It should be noted that only hard particles or the fundamental particles
of the atom, are hollow. All other particles, including photons, do
not have this tendency because of the nature of their formation. If the
softer particles were hollow, they would be unable to capture harder
particles. Hard particles entering a hollow, soft particle, would
maintain their charges and force a mutual repulsion. Therefore, they
would escape immediately. Photons, if hollow, would tend to be less
stable, and the probability of forming other particles would be
lessened.
When a soft particle disintegrates, a chain reaction occurs. The
disintegration releases the confined, harder particles. The energy
released during the disintegration is generally sufficient to
disintegrate the weaker hard particles which it originally captured.
This, in turn, results in the disintegration of still harder particles,
until the very hard and stable electrons of electricity are released.
Highly interesting experiments performed in Poland by two scientists;
Howsky and Groot, demonstrated the ability of soft electrons to house
and camouflage harder electrons, and to release them under certain
conditions. These experiments were also a great confirmation of other
principles already mentioned here, especially those involved with
levitation.
A small quartz crystal was attached to an oscillator which generated
radio frequencies of several kilowatts. This caused the crystal to lose
it’s transparency and increase it’s volume 800%. The crystal then
levitated and carried the oscillator, as well as a 55 pound weight, to a
height of two metres above the floor. An account of this was given in
an issue of Science and Invention magazine and it included a photograph
of the levitation.
19. The energies concentrated inside a pyramid have been shown to
be extremely beneficial to humans. Soft particle bombardments from
outer space and especially from the Sun, concentrate inside the pyramid.
Some, passing through the surface of the pyramid are slowed down to
such an extent that the Earth’s gravitational field, repelling the
negative charges, tends to keep them inside until collisions with other
particles drives them out.
Most of the particles collected by the pyramid, concentrate along the
edges as would be expected, since electricity on any charged body tends
to do much the same thing, with concentrations at points and along
edges. In fact, pyramid frames have been found to be nearly as
effective as the closed pyramid, if, and only if, there is a continuity
in the framework and no breaks in any of the joining parts.
The soft electrons collected on a pyramid frame or closed pyramid, soon
reach saturation point and continued bombardment causes the excess to
drop down inside the pyramid. This, coupled with the gravity-repelling
forces, causes a high concentration inside the pyramid. The proportions
of the pyramid are apparently a factor in it’s performance. If the
sides are too steep, many of the soft electrons will move along the
edges into the ground outside instead of being forced inside the
pyramid. If the sides are not steep enough, not many particles will be
collected as they strike the material at nearly a right angle which
causes only a small reduction in velocity. If they strike at a sharper
angle, there is a greater tendency for them to be retained by the
material.
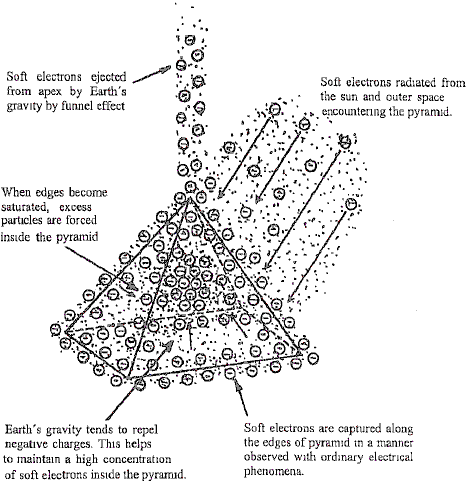
f two sides of the base are aligned with magnetic North, it is allegedly more effective. Pyramids can be rendered more potent by lining the interiors of a non-metallic enclosed pyramid, with metal foil such as aluminium or copper. The foil allows a greater quantity of soft electrons to accumulate around the non-metallic outer portion because the soft particles do not pass through the metallic substance as easily, causing a back-up of soft particles. During the process, the foil absorbs large quantities of soft particles before many of them can enter the pyramid. pyramids also radiate soft electrons upwards from the peak.
Many of the soft particles which are stopped briefly on the outside of the pyramid, are repelled upwards by the Earth’s gravitational field, and as well, by soft electrons attached to the pyramid. This produces a funnelling effect which ejects soft electrons from the apex of the pyramid. The Earth’s gravity accelerates soft particles at a far greater rate than it does ordinary matter as soft particles are associated with ethers which are much closer to those of the gravity-inducing particles than is the case for ordinary matter. After the pyramid becomes saturated, a greater quantity of soft particles than ever, will concentrate inside. The foil will continue to radiate a high concentration of soft particles during the night when the number of particles bombarding the pyramid is considerably reduced.
It is found that pyramids work better during the summer than at any other time of the year. They are also more effective in the lower latitudes because most of the energy concentrated by the pyramid comes from the Sun. There are conflicting opinions as to the effectiveness of pyramids because of this as there is little understanding of the principles involved. For example, those who experiment with pyramids in Canada may claim that they don’t work while those in Southern California will contradict them. A pyramid does not increase the flow of soft particles through the area covered by the pyramid as the same concentration flows outside the area. What a pyramid does, is impede the general flow of soft particles and produce a back-up of particles inside and below the pyramid, and consequently, a higher concentration of soft electrons in these regions. The material used in a pyramid is of great importance. This was demonstrated when a wealthy man in the Midwest built a pyramid-shaped house five stories high, which was then covered with gold-plated iron. The phenomena produced were completely unprecedented. For example, ground water was forced to the surface and flooded the first floor. This was because the soft particle concentration inside and below the pyramid was so great that ground water was impregnated with such an abnormal concentration of negative charges that it was repelled upwards by the Earth’s gravity.
Gold atoms have extremely high positive electrostatic field effects, more so than any other atom. This is why gold is the most malleable of all substances. This means that soft electrons will have a greater affinity for gold than for any other metal. As a result, abnormally high concentrations of soft electrons will concentrate around gold. This effect is greatly enhanced when gold is in contact with iron. These dissimilar metals produce an EMF which is turn, causes a flow of electricity or eddy currents resulting in the iron being magnetised. The magnetic field produced, captures additional soft electrons. A higher concentration of soft electrons is created by this combination then could be produced by a similar thickness of gold foil alone. It follows that by far the most effective material that could be used for pyramids is gold-plated sheet iron (galvanised iron should not be used).
With everything else being the same, the greater the size of a pyramid, the better the performance. The reason for this is that the thicker the layer of concentrated soft electrons through which the incoming soft particles must pass, the more they are slowed down when passing. This results in a greater back-up of soft electrons and an increase in the concentration inside the pyramid. Another reason is that a large pyramid has a greater ratio of volume to surface area. Soft electrons are continuously leaking away from the surface of the pyramid, the larger the pyramid, the lower the percentage of soft electrons which is lost. Consequently, very small pyramids are ineffective.
20. Viktor Schauberger of Austria was puzzled by the fact that large mountain trout could remain motionless for as long as they liked in the fastest flowing water in streams. When disturbed, they escape upstream with fantastic speed. He also noticed that water gets charged up through swirling vortex action as it flows around obstructions. As the water is highly agitated, it gives up large quantities of hard and soft electrons to the fish, causing the entire outer surface of the fish to get a high negative charge. This charge repels the outer electrons of the water molecules, totally eliminating drag and as a result, the water exerts almost zero force on the fish. This effect is even more enhanced as the fish moves upstream, much more so than if the fish went downstream. The negative charge also helps the fish jump as the Earth’s gravity boosts it upwards.
21. Brown’s gas, produced by one form of the electrolysis of water has properties which seem bewildering to most scientists. Using it, allows steel to be welded to a clay brick and the flame is not harmful to human flesh. The flame temperature depends entirely on what it is applied to. It can also reduce nuclear radiation by 96%. The properties of Brown’s gas confirm the information above. Water has a very large capacity to store soft electrons in addition to those already present in the structure of water. Brown did not separate water into hydrogen and oxygen. Instead, he added additional soft electrons to the water molecules. These additional charges greatly weakened the cohesive forces between the molecules, converting the water to an unstable gas. All of the properties of Brown’s Gas follow naturally from this. Under welding conditions, the vast concentrations of soft electrons supply the release of sufficient quantities of hard electrons to produce the needed heat. In addition, the soft electron concentrations enable iron atoms to partially interpenetrate brick molecules to produce a bond between brick and iron. Also, with the ultra-high concentration of soft electrons, the gas can readily neutralise the positive charges of nuclear radiation.
22. We need to examine the source of the Sun’s radiant energy. One thing that all suns seem to have in common is their great size. The astrophysicists speak of white dwarf suns of planetary size or less. It is clear that any claims made by astronomers or astrophysicists concerning celestial determinations, have about the same degree of merit as the other scientific claims which have already been mentioned. There is nothing to justify the existence of a white dwarf. For one thing, due to it’s allegedly small size and limited gravitational influence, it could only hold very small bodies of asteroid size in orbit around it and those would have to be only a short distance away from it. According to the fallacious theories of orthodox science, a white dwarf consists of atoms with practically all of their electrons stripped away, giving it enormous gravity. It will be shown that astrophysicists have no way of accurately determining the distance or the size of any celestial body.
The larger the body, the greater it’s mass or volume in proportion to it’s surface area. This means that as the size increases, it is less probable that the energies produced by the normal activity of the atoms in the body’s interior will escape from the surface without a resulting increase of temperature at the surface. The energy radiated from the surface will be in the form of photons and other particles of all types. Below a critical size, the surface area is sufficient to allow all of the radiant energy created in it’s interior, to escape without an increase in temperature. In fact, such a body will lose heat unless it receives sufficient energy from it’s surroundings.
As a body increases in size, it’s surface area becomes increasingly inadequate to allow the radiated energy in it’s interior to escape without a build up of heat at, and below, the surface. The surface will not radiate the heat or energy outwards as quickly as it is created in the interior. The rate at which energy is radiated from a surface increases rapidly with a resulting increase in surface temperature. This varies as the fourth power of it’s absolute temperature. For example, within a certain temperature range, if the temperature is doubled, the rate at which energy is radiated in the form of photons and soft particles, increases by a factor of 16.
The critical size of such a body will depend on it’s composition. For example, if it contains a high concentration of mildly radioactive substances, this critical size will be less. If the body is hollow, then the dimensions would have to be greater. The red giants, if they are even close to the dimensions claimed, would have to be hollow and have relatively thin shells, otherwise, they would not be red as their surface temperatures would be astronomical.
The actual source of the energy which is finally radiated out into space is the soft particles and photons which are normally radiated by the atoms of the material inside a sun. This is due to the activities of the fundamental particles. Because of the great mass of a sun, an abnormal concentration of these soft particles is always present in the interior. This concentration is greatest near the surface. There is a steady increase in intensity, from the centre toward the outside. This results in a continuous disintegration of a high percentage of those particles near the surface, accompanied by a great increase in temperature, which in turn, results in a greater rate of disintegration, with the release of harder particles which produce the higher temperatures. At the same time, there is an increase in the rate at which the soft particles are created. The temperature will decrease steadily as the centre is approached and any sun will have a relatively cool interior.
The principle that size is the major factor in a celestial body’s ability to radiate is confirmed by the behaviour of very large planets such as Jupiter and Saturn. An application of this principle indicates that bodies of such size should start radiating more energy than they receive from outside sources. Recent determinations indicate that Jupiter and Saturn do, in fact, radiate more energy than they seem to receive from the Sun. A probe showed a surprisingly higher temperature in Jupiter’s upper atmosphere than was formerly believed to exist.
It now becomes apparent that the conventional theory which states that the radiant energy of the Sun is produced by thermonuclear reactions is complete nonsense. One thing to consider is that if this were the case, the Sun’s radiation would be so lethal that no life could exist on any of the planets in the solar system.
Occasionally, throughout the universe, the gradual build up of heat in the interior of suns becomes very much greater, possibly due to the quantity of radioactive elements in the interior caused by transmutation. In such cases, relief valves in the form of sunspots, no longer take care of the excess energy increases and large portions blow apart, releasing astronomical quantities of radiation. After the explosion, the supernova becomes a burnt out body in comparison to it’s former state. Considering the countless billions of stars within our field of vision, and since only a few supernovas have been observed down through history, it is logical to conclude that it is not the fate of the great majority of stars.
One of the phenomena concerning the Sun, which completely baffles all of the scientists, is that it seems to rotate faster at the equator than it does in the higher latitudes. Sunspots in the vicinity of the equator make a revolution about the Sun in less time than those in the higher latitudes. This is an annoying paradox which can’t be pushed aside by these scientists as it is out there for all to observe.
The part of the Sun which we see is a highly fluidic blanket. The region around the Sun’s equator could rotate faster if, and only if, a steady external pull is exerted on that region. Otherwise, internal friction would eventually produce a uniform motion. This means that bodies in orbit near the equator and close to the surface, are generating a high concentration of gravity-inducing radiations. It becomes evident that such bodies could not consist of normal matter and are probably composed of atoms and molecules made up of softer particles which are little affected by the Sun’s radiation. Such bodies could generate a concentration of gravity radiations considerably out of proportion to their masses. Being constructed of this kind of material, they would be practically invisible.
23. Errors have been made in determining the size and distance of planetary bodies. Charles Fort cited many instances of fiascos which belied astronomers’ claims of extreme accuracy in determining stellar and astronomical distances. His revelations did little to enhance their reputations as paragons of integrity.
The principles employed by astronomers in their measurements are essentially the same as those used by surveyors in measuring distances and elevations. However, some surveyors admit that they are unable to determine the height of mountains with any degree of precision and their measurements may be off by as much as 10%. Mr Cater has tested this using an altimeter which was set to zero at sea level and then driven to the top of a mountain at 42o 30’ North latitude, which is supposed to have an elevation of 9,269 feet. The altimeter reading agreed closely with the established elevations of towns along the route ranging from 1,000 to over 4,000 feet. However, at the top of the mountain, the reading was only 8,800 feet. Mr Cater then reset the altimeter to the 9,269 feet attributed to the mountain and retraced his route. At every spot on the return trip, the altimeter consistently indicated elevations more than 400 feet higher than before. Even after several months, the altimeter reading was still more than 400 feet higher than it should be. A similar test was carried out on a mountain with a recorded elevation of 4,078 feet and at the top, the altimeter showed 3,750 feet although it agreed with other established elevations much lower down.
The fact that the altimeter was accurate at all places except the top of the mountain (whose official height was found by triangulation) shows that the methods employed by surveyors and astronomers are far from being accurate. The heights of mountains determined by triangulation will always be considerably more than the true value. There are two factors involved. First, the atmosphere becomes steadily denser as one descends from the top of the mountain. Second, the orgone concentration becomes greater closer to the ground. This means that light rays from a mountain top will be refracted and so appear to be originating from a point well above the top of the mountain. This was also confirmed by a barometric test at the top of Mount Everest which indicates that it is actually 27,500 feet in elevation and not the 29,000 feet previously supposed.
A friend of Mr Cater had his property surveyed to determine the acreage. Afterwards, he checked some of the distances determined by triangulation, using a tape measure, and found significant errors. Refraction of light is clearly throwing triangulation results off. The bulk of refraction effects are caused by orgone concentration. The measurement of mountain elevations taken at different times give different values and this is due to fluctuations in orgone concentrations, which are higher on hot sunny days than on cool cloudy days. Also, they are generally higher during summer months rather than at other times of the year.
The examples above show the unreliability of results obtained by triangulation. Astronomers are faced with additional factors when they try to apply triangulation, such as the Van Allen Radiation Belt, varying concentrations of orgone throughout space, etc. It is not realistic to assume that astronomers can determine planetary and astronomical distances with great precision.
There are several factors which astrophysicists and astronomers have not taken into consideration in their calculations. Perhaps the most important of these is the fact that all electromagnetic radiations including gravity in free space, suffer an attenuation effect which is well above that of the inverse square law. Everywhere in the universe is permeated with soft and hard particles of all kinds. These particles have been radiated by planetary systems for countless ages. This principle is demonstrated by fluctuations in the velocity of light and gravity attenuation.
There is a steady decline in the velocity of light as it travels through space. The reasons for this can be seen from the following considerations. Normal light, or light which has travelled a relatively short distance from it’s source, immediately resumes it’s original velocity after passing through a dense medium such as glass or water. As shown earlier, this is due to the close bunching of photons and soft electrons in any given ray. The concentrations of particles in a ray of light tends to decrease after travelling great distances. The father it travels, the more attenuated the ray becomes. This means that its ability to increase it’s velocity after passing from a medium of a given density to one of a lesser density, will be reduced. This is, of course, due to the scattering and dissipation of particles within the ray as it encounters the conglomeration of particles moving in random directions throughout space.
Since conglomerations of soft particles permeate all known space, and the distribution is not uniform, it follows that light will experience refraction effects, even when passing through free space. Therefore, even under the best conditions, with observations being made beyond the atmosphere, astronomical observations cannot be made with any degree of accuracy. The difficulty is, of course, compounded when the observations are made inside the atmosphere. It is small wonder that Charles Fort found a wealth of evidence that completely debunked the astronomer’s claims of great precision.
The fluctuation in soft particle distribution, along with the refraction effects of the atmosphere, rules out the possibility of averaging out errors by making many observations and applying the mathematical method of least squares. Conventional statistical theory obliterates actual small variations and distorts data by such averaging out processes. The gross errors which crop up despite these methods speak for themselves.
In order to measure the orbital distance of various planets, it was necessary to find the distance of the Earth from the Sun. Originally, this was allegedly found by measuring the angles that two widely separated observation points on the Earth made with the Sun. This is known as the parallax method. The distance to the Sun was calculated from these angles and the distance between the observation points. The size of the Sun could then be determined, and knowing the orbital period of the Earth around the Sun, the Sun’s mass and surface gravity were calculated by applying the false Newtonian concept of gravitation.
More recently, the distance to the Sun, known as the “astronomical unit” was supposedly determined to a high degree of “precision” by measuring the distance of the body Eros by the parallax method when it was closest to the Earth. Knowing the period of Eros’ orbit, the distance to the Sun was calculated by the use of Kepler’s law which states that “the square of the periods of any two planets are proportional to the cube of their mean distances from the Sun”. Since the orbital periods of the planets are known to a reasonable degree of accuracy, most of the other unknowns within the solar system could be calculated by knowledge of the Sun’s alleged mass and surface gravity. By now, it should be apparent that it would be a miracle, or at least, one of the strangest coincidences ever, if the actual distances coincided even approximately with the calculated values.
If the Newtonian concept were valid and the planets were held in orbit by only the effects of the Sun’s surface gravity, then the orbital periods of the planets would be a reliable means of determining planetary distances. Since it has been proven that the concepts on which these calculations were made are false, it can be safely concluded that the size of the orbits is considerably different from what the astronomers claim. As a result of the dissipation effects of radiation, well beyond that which can be expected from the inverse square law, it follows that planetary distances are very much different from the accepted values.
This excessive attenuation of the gravity effects of the Sun is reflected in the alleged rapid increase of orbital distances of the outer planets. The supposed orbital distances are as follows:
Earth: 1.0 astronomical units. Mars: 1.52 (difference 0.52) The asteroids: 2.76 (difference 1.24) Jupiter: 5.2 (difference 2.44) Saturn: 9.58 (difference 4.38) Uranus 19.16 (difference 9.68) and Neptune 30.24 (difference 11.08)It does not follow that the longer the orbital period, the greater the planetary distance. For example, within certain limits, the larger and more massive the planet is beyond a certain critical amount, the slower it must move in order to stay in a given orbit. This is because the total gravity effects of the Sun are unable to permeate and affect the entire mass to the extent that they would with a smaller planet. For example, a planet like Saturn could be placed in a stable orbit inside Earth’s orbit. Yet it would have to move so slowly in it’s orbit that it’s orbital period would be much greater than that of Earth. This means that orbital periods are not a reliable gauge for relative orbital distances.
Although planetary and stellar distances are completely unknown as far as astronomers are concerned, and at this time there are no reliable means available of determining them, the diameters of some of the inner planets, including Jupiter and Saturn, can be calculated far more accurately than any of the other values in the realm of astronomy. The orbital distances of the planetary satellites in proportion to planetary diameters as well as their periods can be accurately determined. The determination of these constants is not affected to any significant degree by the dissipating factors of light already mentioned since a planet and it’s satellites are about the same distance from the Earth. The main factor which makes it possible to approximate the diameter of any of these planets is the knowledge that they have practically the same surface gravity as Earth does.
If a satellite is very small as is the case with the satellites of Mars, a planetary diameter can be calculated with a high degree of accuracy. In fact, Mars is the only planet in the solar system whose diameter can be reliably determined. Astonishingly, Mars turns out to have a diameter of about 11,300 miles. Using unusual methods, Mr Cater has estimated the diameter of the Sun as over 2,500,000 miles and at a distance of about 277,000,000 miles from Earth. The Moon diameter at 5,200 miles at an average distance of 578,000 miles, shell thickness 115 miles and surface gravity 98% that of Earth. With a lesser degree of accuracy, the diameter of Venus is assessed at 23,000 miles and Mercury at over 8,000 miles. Jupiter diameter about 230,000 miles and Saturn about 200,000 miles. It is most unlikely that the accepted distances to the stars are even approximately correct.
24. Hard electrons travel through metals more readily than through non-metals. This indicates that they encounter more extensive positive electrostatic fields between atoms and molecules than in non-metals. At the same time, the atoms in metals are usually more mobile or free to move around than is the case with solid non-metals. This is why the best conductors of electricity are also the best conductors of heat. It is significant that all of the heavier atoms are metals, with the exception of radon which is a gas. This means that such atoms have a higher net positive charge, which causes a stronger mutual repulsion for greater distances on atoms which are not directly connected to each other. This greater extension of the positive zone around such atoms gives them more freedom without breaking the bond which holds them together. The repulsive forces of nearby atoms, increases the mobility of any given atom.
The heavier atoms contain more protons and neutrons bunched together. The outside pressure needed to hold a group of mutually repulsive particles together is independent of the number of particles present.
One might conclude that the heaviest atoms make the best conductors, but this is not the case. Silver, copper and aluminium are the best conductors although their positive field zones are not as extensive, they have less inertia and so are more easily pushed out of the path of a flow of hard electrons. Electrons which flow along conductors are continually colliding with atoms in motion. Therefore, it require a steady application of electromotive force at the ends of the conductor in order to keep them flowing. The atoms of non-metals are more firmly locked into position and therefore do not have that much of a tendency to move out of the way and this is why they make good insulators. Electrons follow the lines of least resistance and so they tend to move on the surface of the conductor where there is less tendency to collide with atoms.
The rules governing the conductivity of soft electrons are somewhat different from those of hard electrons. Soft electrons are enormous when compared to hard electrons. This can be seen when considering that the average diameter of a particle is directly proportional to it’s so-called wavelength of the light comprising it (or inversely proportional to the frequency). The ethers associated with atoms and their fundamental particles are much higher in frequency than those associated with soft particles. This means that atoms will offer little resistance to the passage of soft electrons. However, the magnetic fields resulting from thermal agitation of certain atoms and molecules are involved with ethers which are closer in frequency to the ethers directly associated with soft electrons. Consequently, soft electrons will interact with these fields. This explains why metals in general offer greater resistance to the passage of soft electrons than do non-metals.
The ordinary electrical transformer presents an enigma. The secondary of the transformer continues to pour out or eject electrons from a seemingly unlimited source. There is a limited quantity of free electrons in conductors which should be exhausted quite quickly. The standard argument used to account for the source of current is that free electrons in the circuit supply the electrons and are used over and over again. A simple calculation demonstrates that free electrons in conductors are not the source of electricity.
Consider a wire two millimetres in diameter which carries about 10 amps of current. The electron flow is concentrated near the surface of the wire. Since the electricity in a conductor travels at about the speed of light, such a wire 186,000 miles long would have 10 coulombs of electricity distributed over it’s surface at any instant. The surface area of this wire is 1,840,000 square metres. A parallel plate capacitor having this plate area and a separation of one millimetre, would have a capacity of 0.016 farads. Even with a potential across it’s plates of 100 volts, it would still only be able to concentrate an equivalent of 1.6 coulombs, and a good part of this electrostatic charge would be due to the displacement of the electrons and protons of the atoms. This voltage is more than enough to concentrate all of the free electrons on the surface of the plates. Similarly, all of the free electrons in the wire example would be involved if the current were maintained with 100 volts. Of course, a wire this long would have too much resistance to carry any appreciable current with 100 volts, but this has nothing to do with the argument just given. As a matter of fact, even 6 volts is far more than enough to produce a current of 10 amps in a wire of 2 mm diameter. Therefore, there aren’t enough free electrons in any conductor to supply any appreciable current. This means that the source of electrons in current flow is not coming from free electrons in the conductor. The conclusion is therefore that the hard electrons somehow manage to get through the insulation of the conductor and flow into the wire from outside.
By the law of action and reaction, since a current has inertia, any change in the primary current of a transformer produces a force in the opposite direction in the secondary. This reactive force produces a disturbance of the ethers which produce the voltage or Electromotive Force as a result of increased ether bombardment. The EMF induced in the secondary winding of the transformer, creates a temporary electric void in the wire which draws all kinds of negative charges to the wire. The softer electrons quickly penetrate the insulation and stop at the surface of the wire as they do not travel as readily through a hard electron conductor. These softer electrons absorb most of the electrostatic forces in the insulation which impede the flow of hard electrons, allowing the hard electrons to pass through the insulation and enter the wire.
Electrical charges, composed of photons in nearly all the frequency ranges, permeate all space, since they are continually radiated by stars throughout the universe. They are no easily detected as they are in the form of conglomerates with the harder particles residing inside the softer ones. The resulting combinations are highly penetrating and it takes something like a voltage induced in a conductor to separate the harder particles from the softer ones. The performance of a transformer can be greatly impaired by completely shielding the secondary winding with a good conductor of electricity such as copper or pure aluminium. This is because the shield tends to impede the flow of soft particles to the secondary. This effect has been verified by experiment.
The terms “EMF” and “voltage” need clarification. The true nature of the phenomena associated with these terms has never been fully understood. All that has been known is that if a conductor is exposed to an EMF, a flow of electricity is produced. Also, voltage is associated with the amount of energy or work which a current is capable of producing. An EMF of a given value can induce a current with a definite voltage. The voltage produced is directly proportional to the EMF impressed on the conductor. Also, the energy of the current is directly proportional to the voltage. The amperage of a current is a measure of the number of electrons passing through each segment of a conductor per second. Since wattage, or the total kinetic energy of this current flow is equal to the amperage multiplied by the voltage, it follows that the amperage is also directly proportional to the energy of the current flow. Therefore, Voltage is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the electrons flowing along the conductor. This in turn, is directly proportional to the square of the average velocity of the electrons. This simple definition of voltage is sadly lacking in all standard textbooks.
An EMF induces an accelerating force on an electron. What is the nature of this force? Basically, there are two methods of producing an EMF. One is by subjecting the conductor to a fluctuating magnetic field, and the other is by exposing the conductor to a difference of potential, such as connecting it between the opposite poles of a battery. In that instance, one battery pole has a negative charge while the opposite pole is positive. The flow of electrons is the result of an electron concentration at one point tending to flow to an area where there is a shortage.
The EMF is produced by direct electrostatic force, which in turn, has a dual nature. There is the tendency for negative charges to be attracted to positive charges, and then there is also the mutual repulsion between negative charges. The voltage attained is directly proportional to the difference of potential existing between the poles of that battery. The difference of potential is equal to the kinetic energy gained by the electrons in moving from one potential to the other.
The EMF produced by a fluctuating magnetic field gives the same results but the process is different. When a conductor is subjected to a fluctuating magnetic field, as with the secondary winding of a transformer, the “free” electrons of the conductor and the outer electrons of the atoms which are not as intimately associated with the atoms, are exposed to differential ether bombardments. It is equivalent to an electrostatic force. When a magnetic field changes, the change does not take place simultaneously throughout that volume of space occupied by the field but it progresses from one portion to another. This creates differential electrostatic ether particle bombardments on electrons within the field. When a conductor cuts magnetic lines as with an AC generator, the electrons are subjected to the same conditions experienced by electrons moving between the poles of a magnet. The accelerating force will be in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the electrons in the conductor are found to move.
If there were even a small fraction of the free electrons existing in the matter as is believed by our physicists, the negative charge effects of matter would be so great that these bodies would be unable to get close to each other. Much of the charge on capacitors comes from outside the capacitor, as is the case with the flow of electricity in conductors. Actually, free electrons in a conductor are practically non-existent. Hard electrons which are not a part of the atoms are captured by soft particles which permeate matter. The soft particles release hard electrons when subjected to the EMF in a current, or the voltage across the plates of a capacitor.
The current in a straight wire is evenly distributed along the surface where the electron flow encounters the least resistance. The released hard electrons which are directly affected by the EMF, tend to move as a unit partially held together by mutual magnetic attraction. This unit leaves a temporary void behind it which is quickly filled by surrounding hard electrons. Many such groups are started almost simultaneously in a conductor at about the speed of light, although the electrons themselves travel at a much lower velocity. When an EMF is applied to a conductor, something akin to the domino effect is set up in the ethers. This effect travels at the speed of light since it is produced in a similar manner.
That the source of electricity flowing in power lines as well as that produced by generators, comes from soft particles which permeate and surround the area, has been proven during auroral displays. When aurora activity is unusually high, transformers in Canada have been known to burn out and even explode. At the same time, increase of current flow in power lines has been great enough to trip circuit breakers as far south as Texas. As explained earlier, the concentration of soft electrons in the atmosphere is greatly increased during auroral phenomena. Some areas receive higher concentrations than others at the same latitude.
A loop of wire or a coil offers impedance to alternating current. This property is known as “inductance”. Since a single loop of wire has inductance, it follows that the effect can be explained in terms of one loop. Electrons tend to travel along the surface of a conductor as that is the path of least resistance. The major source of this electricity is the high concentration of soft electrons which gather around a conductor and permeate the material. This is due to the relatively high positive charge of the conductor. The greatest concentration is found at the surface and a short distance below the surface. When an EMF is applied to the conductor, free electrons are set in motion. During this process, soft electrons concentrated at and just below the surface tend to disintegrate and release more hard electrons. This is enhanced by the concentration of the soft electrons, which is turn causes an agitation of the soft particles, causing them to become highly unstable.
In a straight wire, most of this disintegration and nearly all of the electron flow takes place below the surface. This condition greatly shortens the mean free path of the electrons and the flow stops immediately after the applied EMF is shut off. Consequently, an alternating current will encounter the same ohmic resistance in a straight wire as will a direct current. However, the situation is different when the conductor is looped.
When an EMF is applied to a loop, the free or released hard electrons below the surface are forced to the outside by centrifugal force, whence a still greater disintegration of soft electrons occurs because the greatest concentration is at the surface. The mean free path of the electrons is greatly increased and the flow continues for a brief period after the EMF travelling in the direction of the current flow ceases. When the EMF continues in the opposite direction as in the case of an alternating current, the force must oppose the momentum of the electron flow still continuing in the opposite direction to that of the new EMF direction. It follows that this impedance will be directly proportional to the number of turns and to the frequency of the AC. It is logical to assume that the deceleration rate of the electron flow is a constant when the EMF is zero. This means that the more quickly that the EMF is applied in the opposite direction, the higher the velocity of flow that will be encountered. It will be a linear function.
It would now seem evident that when the AC is rectified of has been changed to a pulsed DC, the coil will produce an increase in amperage where a straight wire will not. Experiments have confirmed this. It was found that the input amperage of a current was greatly increased after it passed through a coil. The increase was greatest during the initial stage of the applied EMF and soon dropped to a lower value as the concentration of soft electrons around the wire was reduced. It follows that a coil will offer impedance only to an AC current. It follows that pulsed DC has numerous advantages over AC. It can be used to operate transformers as well as AC without suffering impedance.
A steady direct current experiences the same resistance in a coil as it does in a straight wire of the same length. The fluctuating EMF produces extreme agitation of the soft electrons around and inside the wire, resulting in the disintegration of a large percentage of them, and the release of a high concentration of hard electrons. This does not occur during the steady flow of direct current. During the initial application of DC there is a surge of additional current during the build-up of the EMF. When the current is shut off, there will be a momentary surge of current in the opposite direction. The excess of electrons on the surface of the conductor and in the coil will naturally flow towards the void outside the coil and in the opposite direction to which the current was flowing. The concepts just outlined can be applied when building a self-sustaining electric generator.
When an alternating current is applied to a coil, the EMF must overcome the impedance each time the EMF changes direction. The greatest amount of resistance occurs at the beginning of each change and then steadily decreases as the current builds up. The resistance will be at a minimum when the current reaches it’s maximum. With AC, the EMF changes direction very frequently and so the maximum resistance is encountered for a high percentage of the time.
The flow of electrons in a wire results in a circular magnetic flow around that wire. As mentioned previously, the magnetic effects between electrons moving together tend to cancel each other out. They are drawn together and the resulting ethers encompass the entire group. This also occurs between adjacent wire segments in a coil. The magnetic effects are cancelled out between the segments and a continuous ether flow, encompassing the entire coil, perpendicular to the direction of the current flow, will occur. The solenoid will then behave like a bar magnet with continuous lines of force.
The Earth’s atmosphere produces geomagnetism in much the same way that a solenoid produces a magnetic field. Changes in the atmosphere move along with the Earth in a circular motion. Although there is little motion of the charges relative to the surface, a magnetic field is still created. Magnetic lines, or ethers, flow from the South magnetic region to the North magnetic region as a result of these rotating charges.
25. Despite the fact that our illustrious physicists have managed to develop as highly a destructive device as a nuclear bomb, they still have no concept of the nature and source of the energy released after a detonation. As with all other well-known phenomena, they try to create the illusion that they comprehend and have explained it. As a matter of fact, academic science has not yet supplied satisfactory explanations for any of the simplest and most common everyday phenomena. The energy released by nuclear devices is explained away by stating that it is a conversion of matter into energy in accordance with the false Einstein relation E = mC2. Many readers, especially those steeped in orthodoxy, may be shocked to learn there is no conversion of mass into energy during such a process, nor by any process in which energy is released! The tremendous heat produced in a nuclear blast means that an abnormal quantity of hard electrons were suddenly released by the complete disintegration of all the soft electrons within the area of the explosion. The intense light that accompanies the blast is the result of the photons set free by the disintegration of those soft electrons.
The key to the triggering of the reaction is the neutron. As indicated earlier, a neutron is equivalent to a collapsed hydrogen atom, and yet it is more than this. A hydrogen atom has a strong net positive charge, while the neutron has no net charge. This means that a neutron has collected far more hard electrons than a hydrogen atom. Since a neutron has no charge, it cannot add to the weight of an atom, as is commonly believed.
The concepts introduced in this treatise render all of the old beliefs concerning atomic structure invalid. The weight of an atom is dependent almost entirely on the number of orbital electrons and the number of protons in it’s nucleus. This will be discussed in more detail later. There is an exception or two to the above rule in the case of certain radioactive elements where the presence of neutrons can actually reduce the weight of an atom. An interchange of excess electrons between protons and neutrons within the nucleus, and thus transformations of protons into neutrons and vice versa, can occur. The neutrons greatly outnumber the protons in the heavier atoms, especially those that are radioactive. During the interchanges between neutrons and protons, excess neutrons disintegrate into protons and hard electrons are ejected from some of the atoms. This results in a transformation of such atoms. Simultaneously, the tremendous interactions between electrons released in this manner as well as from the disintegration of soft electrons in the vicinity cause the higher ethers to be disturbed, ultimately resulting in the production of gamma rays.
The isotope of the more common uranium 238 atom known as U235 is lighter yet it is fissionable and more radioactive than the uranium 238. It is lighter because it supposedly has fewer neutrons than the ordinary uranium atom. The opposite is actually the case. The U235 having more neutrons is more radioactive. The greater interactions within the nucleus result in more hard electrons being released, which reduces the overall positive charge of it’s nucleus.
There is a continuous interchange of ejected protons transforming back into neutrons and vice versa among the U235 atoms. A similar but less violent interchange takes place among the atoms of U238. A low percentage of the U238 atoms receive more than their share of these interchanges and thus transform into U235 atoms. Most of the hard electrons released which contribute to such interchanges and transformations is the result of the disintegration of soft electrons which permeate the atoms. It follows that the main contributing factor of radioactivity is the presence of soft electrons which house the hard electrons! Therefore, if the soft electron concentration throughout the vicinity of a radioactive substance is reduced, it will lose much of it’s radioactivity. By now, it has no doubt occurred to the reader, that a Reich cloud-buster pointed at a radioactive material would cause it to lose it’s radioactivity! This has been proven to be the case. For example, a glowing piece of radium stops radiating when it is placed in front of a cloud-buster.
The source of the energy released during a nuclear blast is now becoming clear. When a fissionable material like U235 or plutonium is bombarded with additional neutrons, the increased activity in the nuclei causes even the most stable soft electrons in the vicinity to disintegrate. A chain reaction of soft electron disintegration in areas well beyond the confines of the fissionable material results. All of the hard electrons and protons originally camouflaged by the soft particles are suddenly released. A tremendous gamma ray production also occurs. Adequate quantities of fissionable materials suddenly brought together can result in a sufficient increase of neutron bombardment of the interior atoms to produce such a result. It is known as the ‘critical mass’. The proper fusion of hydrogen atoms can also cause enough soft electron disintegration to produce a similar result. It is now apparent there is no conversion of mass into energy during the process. All of the fundamental particles of the atoms involved remain intact. In fact, there is even more mass following a blast than there was previously, as a result of the additional hard electrons and protons released. Once again, it is obvious that the Theory of Relativity is in no way concerned.
The monstrous hoax fostered on the public by the Defence Department of the Government, now becomes more than obvious. A Reich cloud-buster can completely deactivate nuclear devices for great distances by drawing away the soft electron concentration from the vicinity of such device. In fact, a cloud-buster can be used for downing fleets of planes carrying nuclear weapons. Combustion is also dependent on soft electron concentrations which of course includes jet engines. Therefore jet engines or missiles cannot function in an area affected by a cloud-buster. The fact that a simple cloud-buster can deactivate a nuclear reactor from a great distance has been proven on numerous occasions. For example, during the time Reich was carrying out intensive experiments with a cloud-buster in Arizona in the early 1950s, a large reactor several hundred miles to the southeast quit functioning. This means that hundreds of billions of tax dollars are being funnelled every year to support a multibillion dollar nuclear industry and other related industries which are rendered obsolete by the device used by Reich.
It is evident that the proper use of the cloud-buster could throw modern warfare back to the stone age. Obviously the drawing of soft particles away from any group would completely enervate each individual and even turn him into a block of frozen flesh. Although a cloud-buster could not completely deactivate a particle beam weapon it could bring down any craft carrying such a device before it could get into position. The potential of the cloud-buster is perhaps greater than even Reich himself realized. Since heat is transferred from one body to another by soft electrons which release harder electrons, the cloud-buster can be used as a highly efficient refrigeration system by drawing soft electrons away from a body. It has been made apparent that this simple device can render present fire fighting techniques obsolete. By use of the cloud-buster in the proper manner, the loss of life and property from fire and storms could become a thing of the past. It also provides dramatic proof of the validity of many of the new concepts introduced in this treatise.
Radioactivity was the subject of a ridiculous, if not amusing, fiasco more than two decades ago when two physicists, Lee and Yang, received the Nobel Prize in 1957. The incident, which was given wide publicity, concerned an error in the parity principle. The parity principle has been defined as "a mathematical concept impossible to define in physical terms". How such a concept could have any bearing on physical reality is not made clear. Generally, anything relating to reality can be defined in terms of reality, which is in conformity with the Law of Cause and Effect.
Incredibly, an experiment was devised to test the validity of this great revelation. It was based on the idea that a radioactive substance should eject more particles in one preferred direction, than in any other. Radioactive cobalt was chosen. It was cooled down to near absolute zero and exposed to a powerful magnetic field produced by a solenoid, in order to align the nuclei. Another physicist, a Dr. Wu, had devoted six months of hard work setting up the experiment. Indeed, it was found that more particles were ejected out of one pole of the solenoid than the other. Which pole was it? Of course, it was the pole out of which the magnetic lines flowed. Naturally, the experiment merely demonstrated that particles tend to travel down magnetic lines of force. The excess of particles that came out of the pole were those barely ejected from the atom. They had such a low initial velocity that, regardless of what direction they happened to be travelling initially, the magnetic field would dictate their final direction of travel.
Lee and Yang were accorded every scientific honour, including the Nobel Prize, as a result of this experiment. Instead of giving them the Nobel Prize, the awarding of an Oscar would have been more appropriate. Accompanying the extensive publicity given this comedy act was a photo appearing in a prominent magazine showing one of the recipients pointing to a grotesque mathematical equation containing over 100 terms! He was allegedly explaining the reasoning behind their great revelation.
The great nuclear scare scam should rate as the biggest lie of the century. This fabrication is so colossal even Mr Cater is somewhat embarrassed to admit he was also taken in by it, as everyone else was, except those directly involved in the conspiracy but Mr Cater never questioned it as he had other universally accepted beliefs. The long-hidden truth is this: radiation from radioactive substances is relatively harmless! One can actually swim in water from so-called high level nuclear waste, drink the water and actually thrive on it. Also one can handle pure U235 and even plutonium (the fuel for A-bombs) with bare hands all day long, and suffer no ill effects. Of course excessive exposure to this radiation can be inimical, as can occur from any other type of radiation such as sunlight. The effects, however, are immediate and not long-lasting if the source of the trouble is removed. The popular belief that mutations can result from this radiation that effects future generations, is complete nonsense. A study of the effects on the victims of Hiroshima and Nagasaki bear this out. The only mutations are immediate damage to cells and subsequent malfunctions from ultra-high concentrations.
For the above revelations we are indebted to a courageous and dedicated individual who worked for 35 years in the nuclear industry. He was intimately involved in every aspect of the production of nuclear fuels and the building of reactors. He is Galen Windsor, of Richland, Washington. The so-called lethal nuclear radiations are relatively harmless, with very limited penetration. In 1987, Galen had already lectured in 77 different cities over a two-year period. His credentials are impressive. He has worked in every major reactor decommissioning project in America. He was involved in the analytical process inventory control, which was responsible for measuring and controlling the nuclear fuel inventory for these projects. He has few peers in this field and all of them agree with him but are afraid to speak out. He is one of the world's greatest authorities of nuclear radiation measurement.
He and others did plutonium processing using their bare hands until radiation monitors were installed at every reactor. Rules were laid down as to the amount of exposure to radiation that must not be exceeded. If the rules were not followed, the worker disappeared and was never seen again by anyone. The reason is obvious. If word leaked out that radioactive materials below critical mass were harmless, then there would be widespread pilfering of such products. The Iie that radioactive materials can be handled only with extreme safety precautions must be maintained at all costs. The high-level disposal act of 1982 calls for the permanent disposal of the so-called high level waste 3,000 feet underground. This high level waste consists of reusable uranium fuel and contains useful metal isotopes. Every ton of it is worth about 10 million US dollars.
Enough has been collected to pay off the National Debt. Portland General Electric owns the Trojan reactor and had a storage basin problem. Windsor offered to take all of their spent fuel off their hands. He would ship it, store it, and do everything that needed to be done at no expense to them, if they would give it to him. They told him "Go to Hell, Galen Windsor - we value it more than plutonium or gold. We are going to play the plutonium future ourselves".
Windsor was taken to California in 1965 to help design and build a nuclear fuel reprocessing plant. After it was built in 1973, a presidential order was issued which said the plant was not to be run. At that time, they had 170 metric tons of spent fuel stored in the basin. Also, the maximum allowed exposure was further reduced by a factor of 10. This was the beginning of Windsor's rebellion against "The Establishment". He began swimming in a 660,000 gallon pool containing the spent fuel. The radioactive materials it contained were enough to maintain a water temperature of 100° F and the water would glow with a bluish light in the dark. He discovered that the tank provided good drinking water.
Windsor was also asked about what was in the burial sites of so-called low-level nuclear waste. The answer was that there are no nuclear wastes, only materials produced in a reactor to be recovered and used beneficially. Low-level waste is an excuse for a Federally-mandated non-inspectable disposal system, so that organised crime can get rid of any evidence they want, and that it can never be dug up again. Also, so that no one finds out whose bodies are in those drums. This is what is contained in barrels that are dropped in the ocean.
Windsor also stated, (and he was in a position to know), that in 1947 the United States sent to the USSR all the necessary materials and technology to build A-bombs! This was under the approval of President Truman. In 1949, they exploded their first A-bomb. Later, the Rosenbergs were executed for allegedly turning over nuclear "secrets" to the Russians.
According to Windsor, by 1975 large reactors no longer had a future. They are being phased out. The notorious Three-Mile Island incident was no accident. It did no damage and no one was harmed. But, it did impress upon the public the alleged danger of reactors. Windsor advocated the use of many small reactors systematically distributed. They could be not only used for producing adequate quantities of electricity, but for obviating refrigeration of packaged foods. When briefly exposed to the radiation from such reactors they will keep indefinitely. A Federal energy cartel is the reason that the effective use of many smaller reactors is not implemented. They control the amount of electricity, the availability and the price. Windsor stated that no reactors have been built correctly. In any event, reactors can in no way, match the use of self-sustaining electric generators for electricity, but their use in preserving food is intriguing.
From the above, it becomes obvious that recent publicity concerning the danger of radon gas in homes is another monstrous hoax! It could be mixed with oxygen in sizeable quantities and breathed for long periods without damage.
The question now arising is why are the radiations from radioactive sources relatively harmless? Three types of radiation emanate from them: alpha, beta and gamma rays. Alpha rays consist of helium nuclei or a small group of protons, neutrons and electrons. The number of neutrons and protons are still unknown despite the vaunted claims of nuclear physicists. Since they are totally ignorant as to their true nature, the nature of gravity and soft particle physics, they have no means of determining such values. Beta particles are the hard electrons of ordinary electricity, and gamma rays are negative charges comprised of ether particles in the same range as that of hard electrons. As such, they have no more penetrating ability than a stream of hard electrons and are no more damaging than the hard electrons when they do penetrate. Since they are comprised of the same ethers as atoms and molecules, it follows that they will not penetrate matter as readily as softer particles. This leaves the alpha rays. It has already been shown that positive charges are inimical to living tissues since they tend to absorb the negative charges living organisms require. However, alpha particles also have little penetrating ability for the same reasons as given above, and quickly absorb electrons to become harmless helium gas. Windsor gave demonstrations of such facts at his lectures by use of a Geiger counter.
The capture of large quantities of alpha particles by high concentrations of orgone energy is another matter. Reich termed it deadly orgone energy. The orgone enters the body and releases alpha particles throughout vital organs and produces what is known as radiation sickness. Reich and his assistants had this experience. When the source of the trouble was removed they quickly recovered. Occasionally, deadly orgone can remain in the body and at later periods, release the positive charges at various times, thus causing severe after-effects. This problem can be alleviated by treatments inside orgone accumulators or pyramids after being exposed to the deadly orgone. This is what Reich and his helpers did.
Galen Windsor also stated that the bomb dropped on Hiroshima contained 20 pounds of U235. The one exploded over Nagasaki had 2.5 kilograms or about 5 pounds of plutonium. This values were jealously guarded secrets for a long time. Windsor is likely the first one who has dared reveal it to the public. The author was acquainted with the late Stanislaw Ulam, a mathematician who had calculated the critical mass of these elements for bombs while working on the Manhattan project. It was a deep, dark secret and he would have parted with his life before he would reveal anything so sacred. The degree of the hang-up officialdom has on secrecy is of a magnitude difficult to comprehend, and the steps they have taken to insure it is even more mind-boggling. It is so infantile and childish that there are no words in the English language to describe it adequately.
Radioactive substances such as plutonium, produce their own heat and the larger the mass, the higher the temperature of the mass. This follows identically, the same principle by which the Sun generates it’s energy or the ratio between mass and surface area. The essential difference is that plutonium can do in a few cubic inches what ordinary matter does in a ball 2,500,000 miles in diameter!
Interestingly enough, Windsor looks about 30 years younger than his chronological age would indicate. He also stated he always sustained a healthy tan from his work with radioactive substances. It is significant that Reich and his assistant had a similar experience in their work with orgone energy. It is clear Windsor and Reich were exposed to the same energies, high concentrations of soft electrons. The constant exposure to high orgone concentrations during his working hours is what has kept Galen Windsor young. Of course the high orgone concentrations was produced by soft electrons clustering around the radioactive substances which produced a constant flow of positive charges.
You may wonder why Windsor and certain others could handle radioactive substances with impunity while others have either died or suffered from serious physical problems after being exposed to the radiation. As mentioned earlier, radioactive materials radiate highly positively charged particles which are extremely inimical. Some are absorbed by soft electrons and become DOR (deadly orgone energy). They can enter the body and remain for long periods before disintegrating and releasing the deadly particles. These particles are very sluggish when compared to negative particles including soft electrons.
The victims of radioactive fallout are not exposed for any significant period to high concentrations of positive charges. Also, the area of exposure is very large; consequently, the Coanda effect does not come into play and there is no rush of orgone energy to alleviate the situation as was the case with Windsor when he was directly exposed to ultra high concentrations of radioactive materials. Any victim of radioactive contamination can be cured by being exposed to high concentrations of orgone for extended periods as was Reich and his assistants after experiencing radioactive sickness. They had received a heavy dose of DOR as mentioned earlier. Being exposed to high concentrations of radioactivity is equivalent to being placed in an orgone accumulator.
This is only a summary of part of Mr Cater’s book which has 586 pages. A number of topics are not even mentioned here. Mr Cater also speaks of:
Superconductivity
The properties of Helium at low temperatures.
Mystery spots on Earth, including the famous Oregon Vortex.
Gravitational anomalies.
The origin of the Van Allen Radiation Belt.
The research of William Reich.
Orgone energy.
The Oranur Experiment.
The Reich Cloud Buster (which is also a weapon of major power).
The nature of Radioactivity and Nuclear devices.
Atmospheric phenomena.
Three practical Free-Energy devices.
The great potential of crystals in the obtaining of Free-Energy.
The work of Nikola Tesla with Free-Energy.
The Searle Effect and many other topics.
If you wish to buy a copy of his book, it is supposedly available at these two outlets: here or in the UK here.
So, having absorbed some of what Mr Cater has to say, do you feel that you have been treated fairly, and the true scientific details presented to you as part of your general education?
Patrick Kelly.- http://www.free-energy-info.co.uk.